Antibody Pairing
QYAOBIO provides different antibody pairing for customers in worldwide
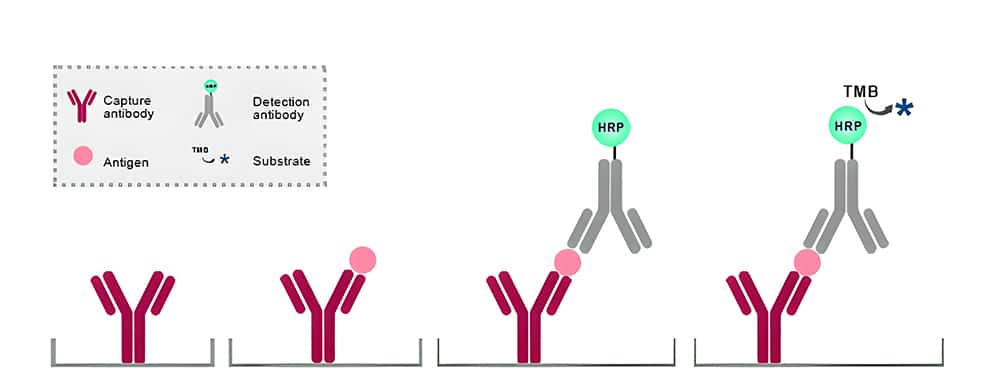
Antibody pairs are two different antibodies generated against the same target that with different binding regions or epitopes. Differential epitope recognition allows both antibodies to bind to the same target simultaneously, making Sandwich ELISAs possible.
Antibody pair can detect and quantify interaction molecules, ensure localization of sub-cellular, reduce the risk of missing weak or transient interactions, improve detection specificity and sensitivity. QYAOBIO has years of expertise in developing antibody pairs, whether creating a monoclonal antibody pair, a polyclonal antibody pair, or a combination, we can provide based on your specific requirements and help you find out the most suitable matched pair for ELISA assay development.
Antibody Pair Principle
The amount of the target bound between a matched antibody pair is measured by ELISA. To start with, a target-specific antibody (capture antibody) is overnight coated to the bottom of the wells of a microplate. The immobilized (capture) antibody is then mixed with samples, standards, or controls in these wells. Therefore, a sandwich is constructed by combining a secondary antibody (detection antibody), and a substrate solution is added that reacts with the enzyme-antibody-target combination to provide a detectable signal. Finally, the intensity of this signal is directly proportional to the concentration of target present in the original specimen.
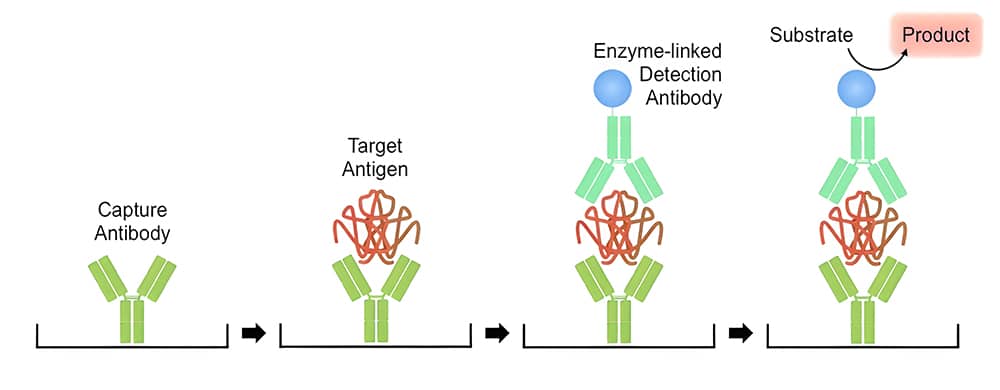
Antibody Pair Production
In order to facilitate subsequent screening, the prepared antibodies should be monoclonal antibodies (mAbs). Hybridoma technology is usually used to prepare mAbs. The experimental process is as shown in the following figure.
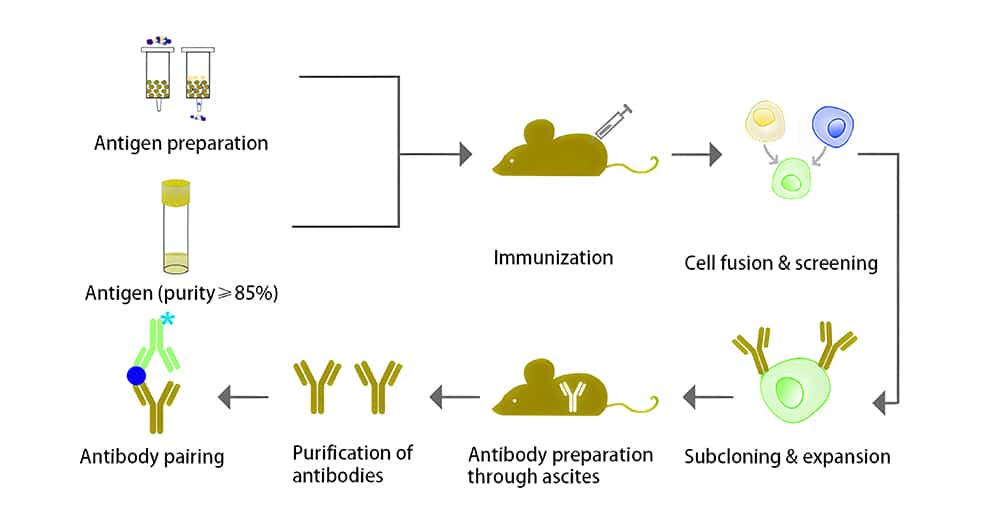
Notice: If there are only a few mAbs, it is likely that no matching antibodies can be found. Therefore, when immunizing animals, we should immunize more animals to obtain more mAbs.
Antibody Pair Screening
The main process of antibody pair screening is three stages:
Selection of Antibodies
Antibody selection is a critical step in the development of immunoassays. Because the choice of antibody largely determines the sensitivity, selectivity, and overall performance of an immunoassay. Qyaobio either employs antibodies that are generated in-house or sources them from a reliable commercial manufacturer.
Conjugation of Antibodies
After the antibodies are selected, they are conjugated to acceptor and donor beads at saturating concentrations. Selected antibodies were tested against each other using a matrix approach. Each antibody is captured on both donor and acceptor beads , then complemented with its pairing antibody in the opposite bead.
Data Collection and Analysis
After conjugating the antibodies to the acceptor and donor beads, assay will be performed by one of our expert technicians, alphalisa assay was performed and quantified using BMG Pherastar reader.
A color-coded matrix will be generated including the alphascreen counts. The client will receive a comprehensive technical report as well as our recommendation for the optimum antibody pair.
Antibodies Selection
One antibody in the pair acts to capture the target and the other acts to detect it. Their function in immunoassays is as follows:
Capture Antibody
The capture antibody is immobilized onto a solid surface, such as a microtiter plate well or a membrane. Then selectively bind to the target antigen present in the sample being tested. Ideally, in order to pull the antigen out of the sample and immobilize it to the surface, the capture antibody should have high binding affinity and specificity for the target antigen.
- In some cases, the ability of polyclonal antibodies (pAbs) to recognize a wider range of epitopes on the target antigen may result in more efficient capture and binding. When the target antigen has multiple different epitopes or is variable in structure, pAbs can be used.
- Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) bind to a single, well-defined epitope on the target antigen with high specificity. As a result, they are perfect for detecting the target antigen in a sample. When high specificity and low probability of cross-reactivity with other molecules are required, mAbs should be considered as capture antibodies. Because of their specific binding, monoclonal capture antibodies can be employed to quantify antigen concentration.
Detection Antibody
Detection antibodies can recognize and detect the bound capture antigen. They are labeled with a detectable marker, such as an enzyme, fluorophore, or radioactive label and added to the sample after the capture step and binds to the captured antigen. In order to ensure accurate and reliable results, they must have high affinity and specificity.
Each antibody type offers distinct advantages, so it is necessary to appreciate the difference and how to use them in different conditions.
- Polyclonal antibodies: Polyclonal antibodies can be used as detection antibodies when conjugated to a label capable of carrying out a detection reaction. In some cases, pAbs can recognize different epitopes on the target antigen, which can lead to increased signaling. Therefore, pAbs may allow more sensitive detection.
- Monoclonal antibodies: Monoclonal antibodies, which bind to a different epitope of the target antigen, can be used as detection antibodies. This enables the formation of an antigen-antibody complex that is recognized by both the capture and detection antibodies, resulting in a higher signal amplitude, and thus the sensitivity of the assay was increased.
More importantly, the choice of antibody type (monoclonal or polyclonal) and use (capture or detection) depends on the specific requirements of the immunoassay in question. In some cases, to maximize assay performance and ensure the required specificity and sensitivity of results, the use of combinations may be appropriate.
Antibody Pairing Applications
Paired antibodies are the basis of many biological experiments, including but not limited to sandwich ELISA, IP-WB, and protein-protein interactions. The application of antibody pairing is shown in the table below.
| Field | Example Analyte(s) |
| Cancer | CEA, PSA, EGF, DKK1 |
| Autoimmune | MMP-1, IL-16 |
| Metabolic Disease | CD-40, IL-6, TNF-α |
| Endocrine | FSH, HPA, ANS |
| Infectious Disease | Ebola, HIV, Adenovirus, Zika |
Moreover, the research of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in the field of the drug development is also to some extent dependent on antibody pairings.
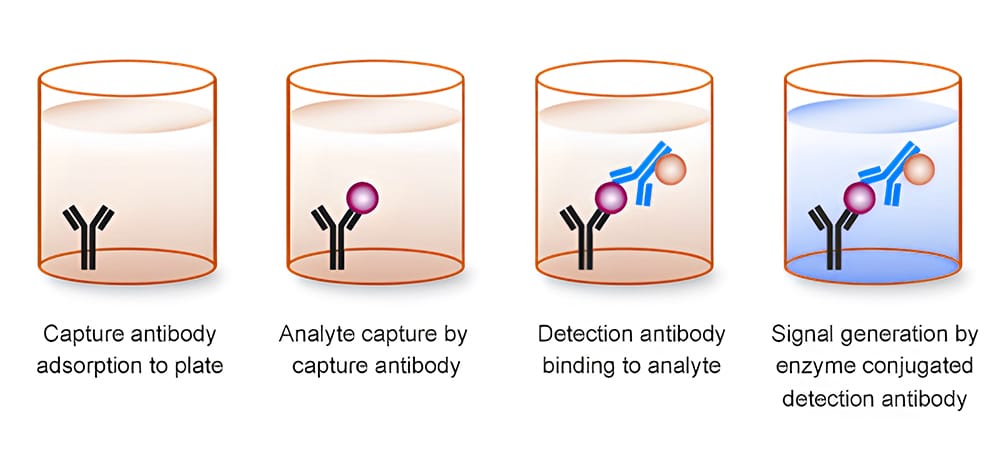
Antibody Pairing Service
Qyaobio is a leading manufacturer and supplier of antibody pairs. We allows you to focus on more important parts of your research instead of the time-consuming effort of searching and testing for the matching antibody components. Our antibody pair can be used in conventional sandwich ELISA or system applications. We offer one stop service including antigen synthesis, preparation of monoclonal antibody, antibody pairing, and mass production of antibodies to support your biological research. You only need to provide antigen or antigen sequences, and we will deliver the paired antibodies.
Call Us
+86(021)-50795728
+86(027)-60707970
