Polyclonal Antibody Production
QYAOBIO provides different polyclonal antibody production for customers in worldwide
Polyclonal antibodies (pAbs) are a type of antibody produced by injecting a specific antigen into lab animal. They are usually generated by different B cell clones in the body and can recognize and bind to many different epitopes of a single antigen. pAbs have a high affinity and specificity for the antigen, making them effective tools in research and diagnostics. They are commonly used in applications such as Western blotting (WB), ELISA, and immunohistochemistry (IHC) due to their ability to detect multiple epitopes on the same protein.
PAb Production Process
Polyclonal antibodies are produced by first injecting a given animal with an antigen, which elicits the immune response that produces antibodies against that antigen. Then purify the polyclonal immunoglobulins from the animal’s blood serum. The production of pAbs involves several key steps.
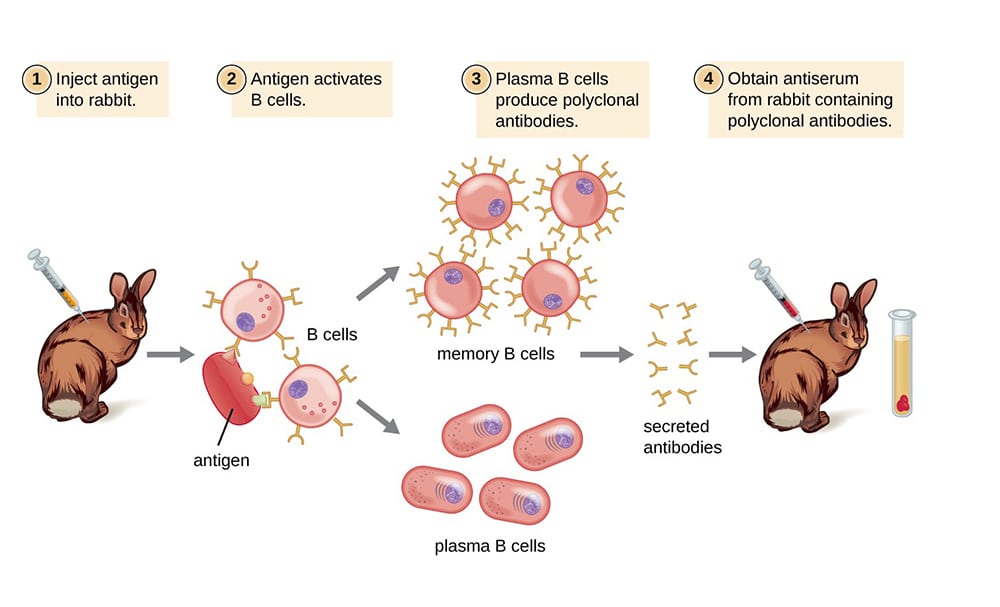
Antigen Preparation
The ability of an antigen to elicit a strong immune response is required to achieve high titers of target-specific antibodies. As a result, selecting a suitable antigen for immunization remains one of the most critical steps in the pAb production process. Several antigens may be used for pAb generation including:
- Proteins: proteins are the most common antigens for generating antibodies. They ensure that pAbs recognize different relevant epitopes naturally exposed in the native conformation of the protein.
- Peptides: since most peptides aren’t immunogenic, adjuvants are typically used to enhance the immune response. Using peptides for immunization is useful in two situations: When developing antibodies for linear epitopes (important in WB applications). When developing antibodies against a specific epitope (increases assay specificity).
- DNA: genetic immunization is only used in special cases. For instance, genetic immunization may be a suitable alternative when the target protein is hard to produce, unstable or contains complex transmembrane domains.
Other antigens, such as small molecules or even whole cells (native or recombinant), may be used for immunization. However, these projects require the development and testing of custom immunization solutions. Qyaobio have the capacity to produce all types of antigens at our facilities including peptides, proteins, DNA, etc. We can also produce polyclonal antibodies using customer-provided antigens.
Immunization
While choosing animal species for pAb production, one should consider the following:
- The amount of pAb desired
- The evolutionary distance between animal species and antigens
- The intended use of pAb
- Prior experience with the immunogens
The production of pAb typically using animals such as rabbits, mice, rats, guinea pigs, goats, or sheep. Rabbits are utilized more frequently since they are genetically divergent from the human and mouse sources of the proteins most often studied.
In order to enhance the immune response, the antigen is typically mixed with an adjuvant such as Freund’s adjuvant. The adjuvant will assist to stimulate the immune system, and result in a stronger antibody response.
Serum Collection
After immunization, the animal’s blood is collected to obtain serum containing the pAb. Then the serum is subjected to an initial screening test to determine the titer of the antibodies. The antibody titers is the concentration of antibodies in the serum.
Purification
Protein A/G affinity purification can enrich Immunoglobulin G (IgG) in the raw antiserum and remove the bulk of unwanted proteins. However, unspecific antibodies with a low affinity towards the target are not eliminated with this type of purification. This will significantly increase the background noise in immunoassays.
Antigen-specific affinity purification is often used to isolate specific pAb from antiserum. It eliminates the majority of the non-specific IgG fraction, while enriching the fraction of immunoglobulin that specifically reacts with the target antigen.
Quality Control
After purification, quality control testing is performed using the procedures listed below to ensure the quality of the pAb.
- Concentration: Absorption at 280 nm
- Purity: SDS-PAGE
- Titer: ELISA
Finally, labeling polyclonal antibody with HRP or biotin provides sensitive enzymatic detection in IHC. It has the flexibility of using a variety of conjugated avidin respectively.
PAb Advantages & Disadvantages
The advantages and disadvantages of pAb were mainly depended on their multi-epitope specificity. The key advantages and disadvantages are listed below:
Advantages
- Inexpensive and relatively quick to produce.
- Highly stable and tolerant of pH or buffer changes.
- High affinity: since pAb can bind to multiple epitopes, they can amplify the signal of the target protein with low expression levels, which is also beneficial to obtain better results in immunoprecipitation (IP) and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) experiments.
- Less sensitive to changes of antigen. Because pAb do not rely on a single epitope, they are more tolerant of minor antigen changes (such as polymorphisms, glycosylation heterogeneity, or slight denaturation) than monoclonal antibodies.
- Easy to couple with antibody labels and rather unlikely to affect binding capability.
Disadvantages
- Prone to batch to batch variability.
- Generates large amounts of non-specific antibodies, which may result in background signal in some applications.
- High chance of cross-reactivity due to a recognition of multiple epitopes.
Polyclonal Antibody Applications
Polyclonal antibodies find an array of applications in both clinical and research settings, making them valuable in various fields. Some of their key applications include:
Diagnosis
Polyclonal antibodies are utilized to detect the presence of specific antigens in various diagnostic tests. For instance, pAbs capture and detect antigens of patient samples in ELISAs.
Western Blot
In Western blotting, pAbs detect specific proteins in a sample based on their molecular weight. Antibodies are able to bind the target protein, and observe its presence.
IHC
In IHC, pAbs detect the presence and distribution of specific antigens in tissue sections. This method is commonly applied in pathology research.
Research
Polyclonal antibodies are used to investigate the presence and localization of specific proteins within cells or tissues, which is a crucial aspect of scientific research. This is beneficial to comprehend protein expression, cellular functions, and disease mechanisms.
Therapeutics
In therapeutic applications, monoclonal antibodies are more commonly used. But pAbs have also been employed in some medical treatments. They are frequently used when a combination of antibodies with various specificities is required, such as in snake antivenoms or certain immunoglobulin therapies.
Competitive Poly-Antibody Service
Qyaobio provides comprehensive pAb production services in a variety of species. Our antibody production services were designed for maximum quality and production yield, from antigen design to serum purification. Standard protocols are available for each species, or we can follow your specific protocol.
In addition, our procedures are fully documented, allowing complete traceability. Let Qyaobio help you develop the ideal polyclonal antibodies to accelerate your research progress.
Call Us
+86(021)-50795728
+86(027)-60707970
