C Terminal Modification
C-terminal modification can increase the bio-activity, rise the stability, prolong shelf life.
QYAOBIO provides multiple options of C-terminal modification to satisfy various research needs. C-terminal modification can create synthetic peptide with exact conformation for specific applications.
The C-terminal is synthesized as an amide to neutralize the negative charge of the C-terminal COOH. C-terminal modification can prevent enzyme degradation, mimic native protein. Therefore, C-terminal modification can increase the bio-activity, rise the stability, prolong shelf life of peptides. Furthermore, this modification also can remove hydrogen bonding in peptides, in order to eliminate interference in the assays.
C-terminal Modification Service
The following are our common C-terminal modifications, but not limited to the following:
- Amidation
- Hydrazidation
- Biotinylation
Classification of C-terminal Modifications
C-terminal modifications are performed for various applications in research and study. The common compounds for C-terminal modification are as following:
AMC
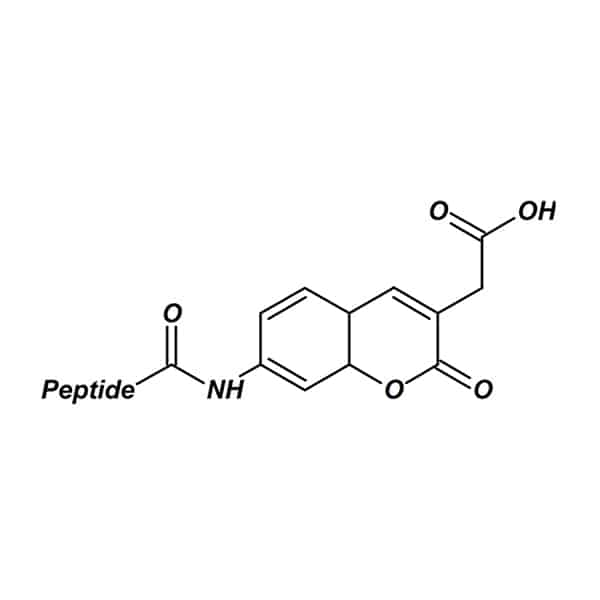
AMC (7-Amino-4-Methylcoumarin) links to the peptides by an amide bond forming between the coumarin amine and the carboxyl group on the C-terminal residue. AMC based enzyme substrates are popular tool for studying of protease activity and specificity. Moreover, the proteolysis of amide bonds will release free AMC, and result in great increase of fluorescence. The common excitation/emission wavelengths are 342/441 nm.
Amidation
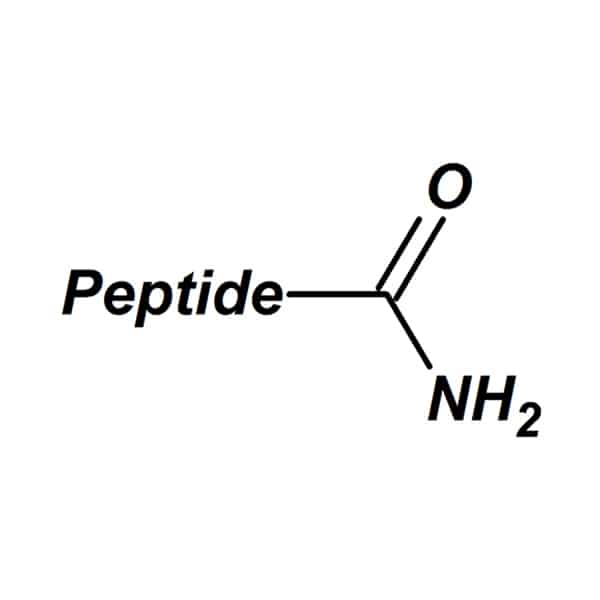
C-terminus amidation can remove the positive charge and encourage peptides to imitate nature structure. In addition, this amidation will increase stability in enzymatic degradation.
Aldehydes
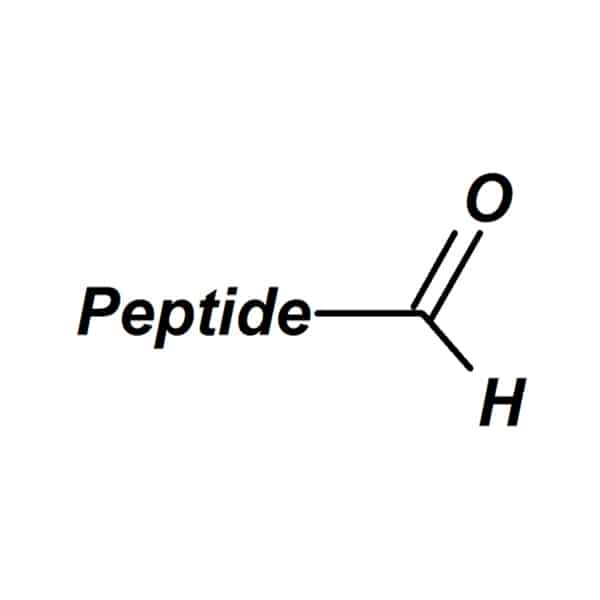
This modification alters the peptides to be reactive intermediates, for examples, the unnatural chemical ligation with hydroxylamine or hydrazine.
Hydrazidation
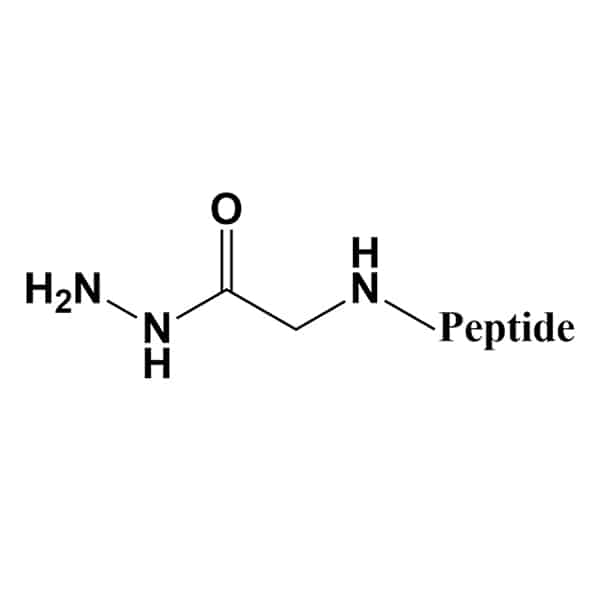
The hydrazidation on C-terminal creates specific structure, especially in aspartic protease inhibitors. The availability of modified peptides are depended on peptide specifications.
Chloromethyl Ketone (CMK)
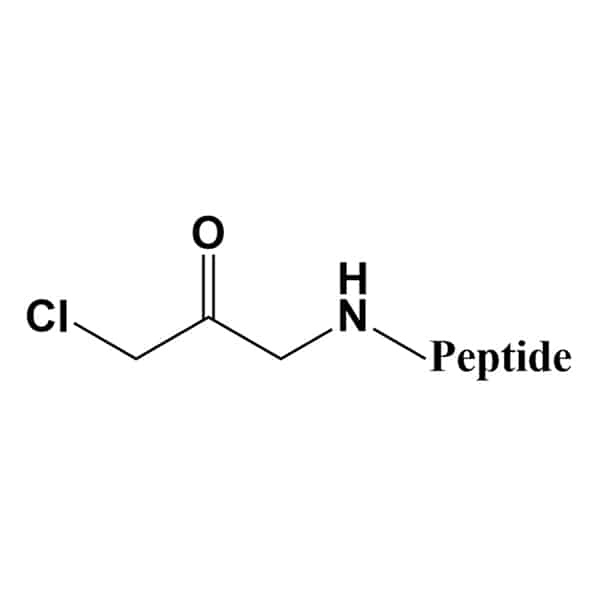
Chloromethyl ketone (CMK) is an irreversible protease inhibitor. The availability of modified peptides are depended on peptide sequences.
Hydroxamic Acid
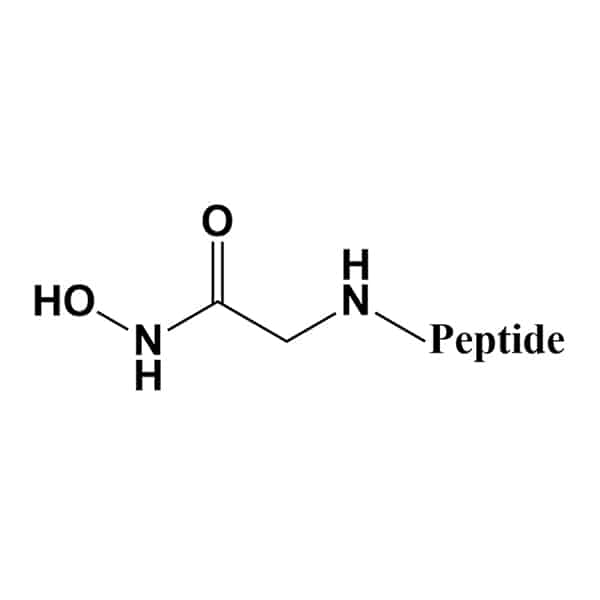
Hydroxamic acid modified peptides are zinc and iron binding structure motif in protease inhibitors, like inhibitors of MMPs, HDAC.
KLH & BSA & OVA
Carrier proteins like KLH, BSA, and OVA can conjugate to the C-terminal of peptides through the inserted N-terminal cysteine. Peptides coupling with KLH, BSA, OVA can significantly increase the cell-mediated immune response, and are applied widely for immunization.
Multiple Antigen Peptides
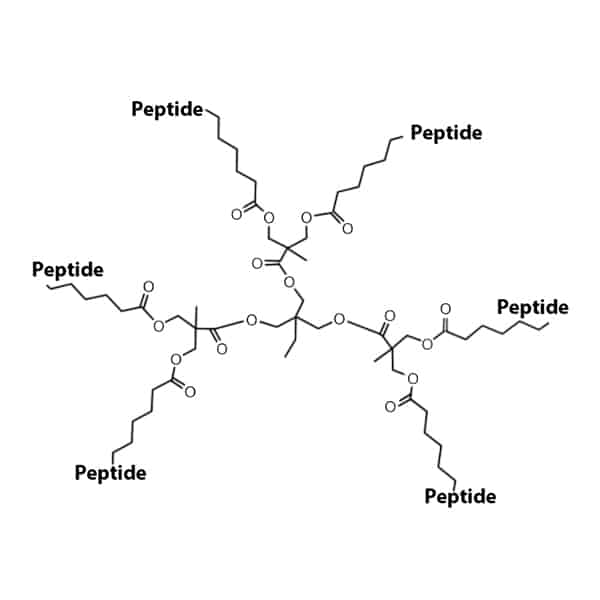
Multiple antigen peptides are the effective method for producing high-tier anti-peptide antibodies and synthetic peptide vaccines. This method applies the α- and ε-amino groups of lysine to form a backbone with multiple peptide chains. According to the number of lysine layers, there are different numbers of peptide branches in synthesis. This modification eliminate the conjugation requirement to the protein carrier.
P-Nitroanilide
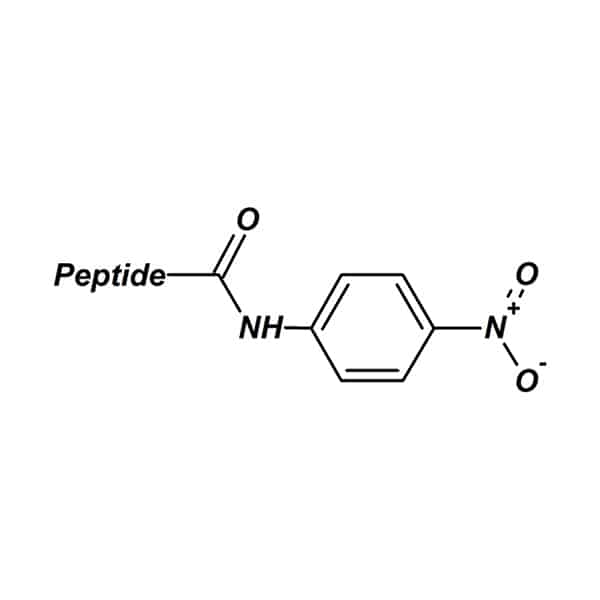
The peptide p-nitroanilide is a compound for study and research of protease activity. Through the proteolysis process, yellow free p-nitroaniline is released from these substrates.
Biotin
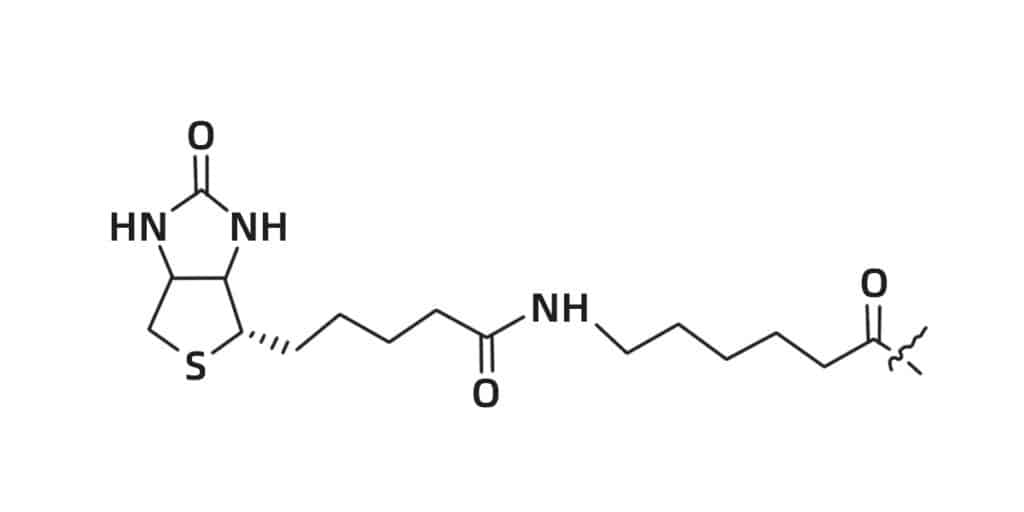
Biotin has strong affinity for both streptavidin and avidin, the biotinylation of peptides is an effective technology for specific peptides binding to streptavidin-coated surfaces. Peptide biotinylation can be synthesized at both N- or C- terminus. At the C-terminus, the first-order epsilon amino group on the lysine is biotinylated to remove the positive charge of lysine.
Esters
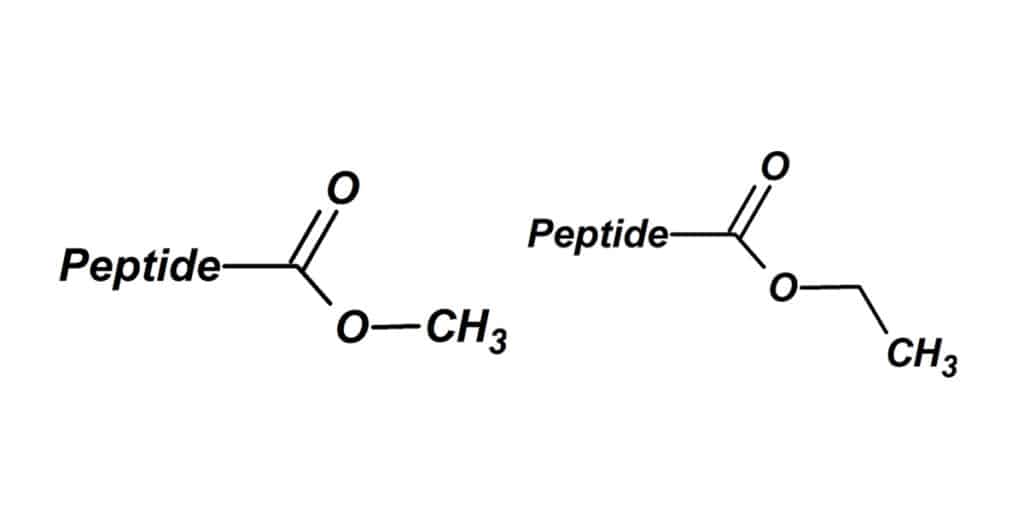
The esterification of peptides is a common C-terminus modification method.
QYAOBIO has excellent experience in custom peptide synthesis of C-terminal modification, we provide confidential and efficient service at competitive price. Every synthesis step is subject to our stringent quality control.
Call Us
+86(021)-50795728
+86(027)-60707970
