Annexin
Annexins (ANX) are abundant cytoplasmic proteins, which bind Ca2+ and interact with phospholipids in a Ca2+-dependent manner. They are mostly found in eukaryotic organisms but largely absent in prokaryotes and yeasts. Annexins are involved in a range of membrane-related events, including organization of membrane domains, linking the membrane to the cytoskeleton, vesicle transport and, in epithelial cells, maintaining cell polarity.
The basic structure of an annexin is composed of two major domains. The first one is located at the COOH terminal and is called the core region. This domain made up of four similar repeats, each approximately 70 amino acids long. Each repeat is composed of five α helices and usually contains a characteristic ‘type 2’ calcium binding sites that are critical for interacting with phospholipids at the plasma membrane. The second one is located at the NH2 terminal and known as the head region. This region precedes the core and plays an important role in mediating the interaction of annexins with other intracellular protein partners.
Notice: All peptides are only for research purposes, Not for clinical use.
Annexin Peptides
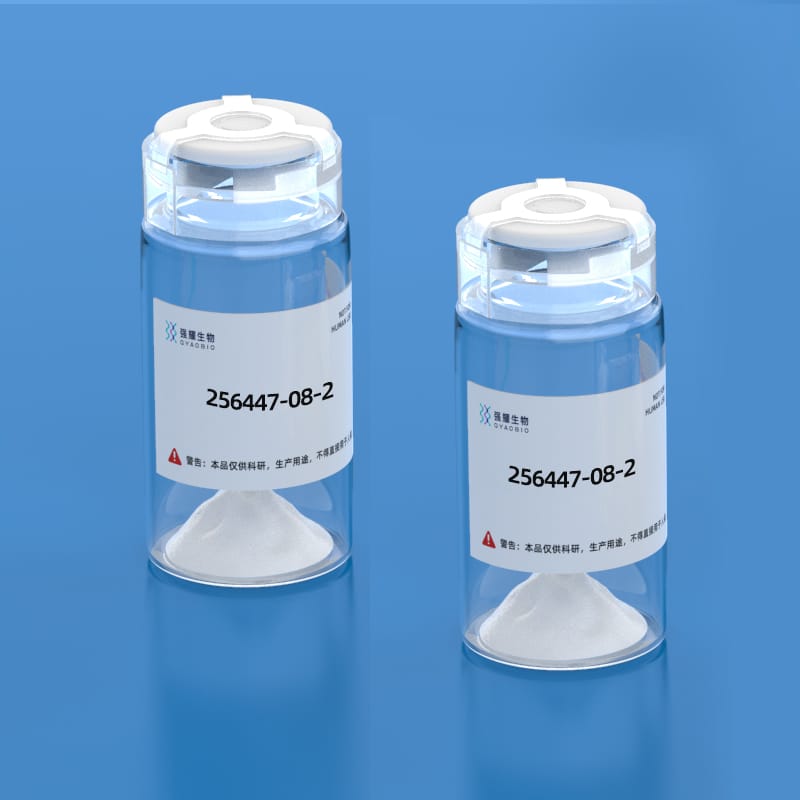

- Name: Annexin A1 (1-11)
- Sequence: Ac-AMVSEFLKQAW
- CAS Number: [256447-08-2]
- Formula: None
- Characteristics: None
- Reference: None
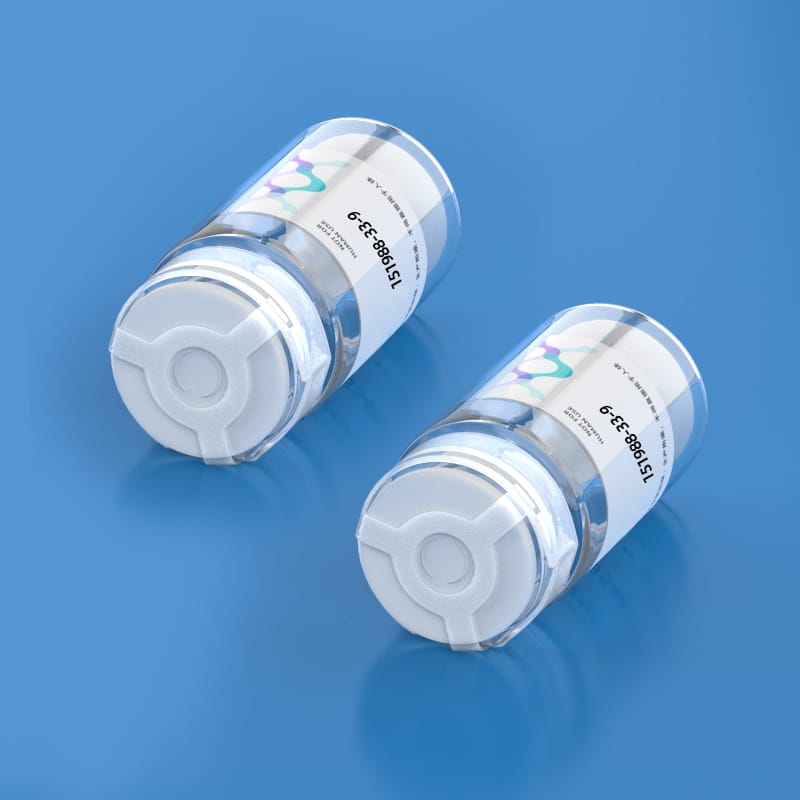

- Name: Annexin A1 (1-25)
- Sequence: Ac-AMVSEFLKQAWFIENEEQEYVQTVK
- CAS Number: [151988-33-9]
- Formula: None
- Characteristics: None
- Reference: None
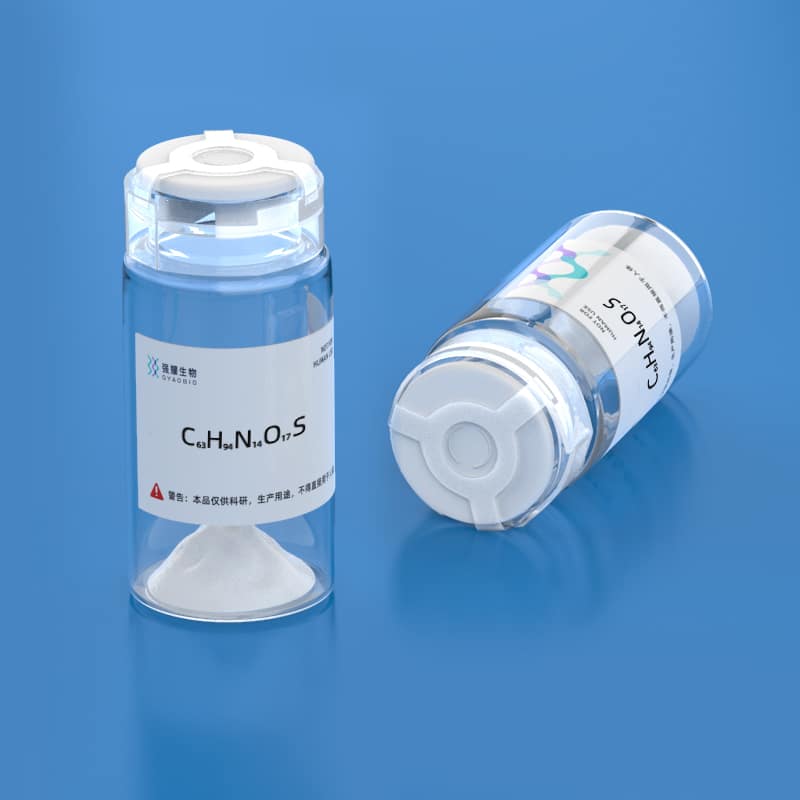
- Name: Annexin 1
- Sequence: Ac-AMVSEFLKQAW
- CAS Number: None
- Formula: C63H94N14O17S
- Characteristics: None
- Reference: None
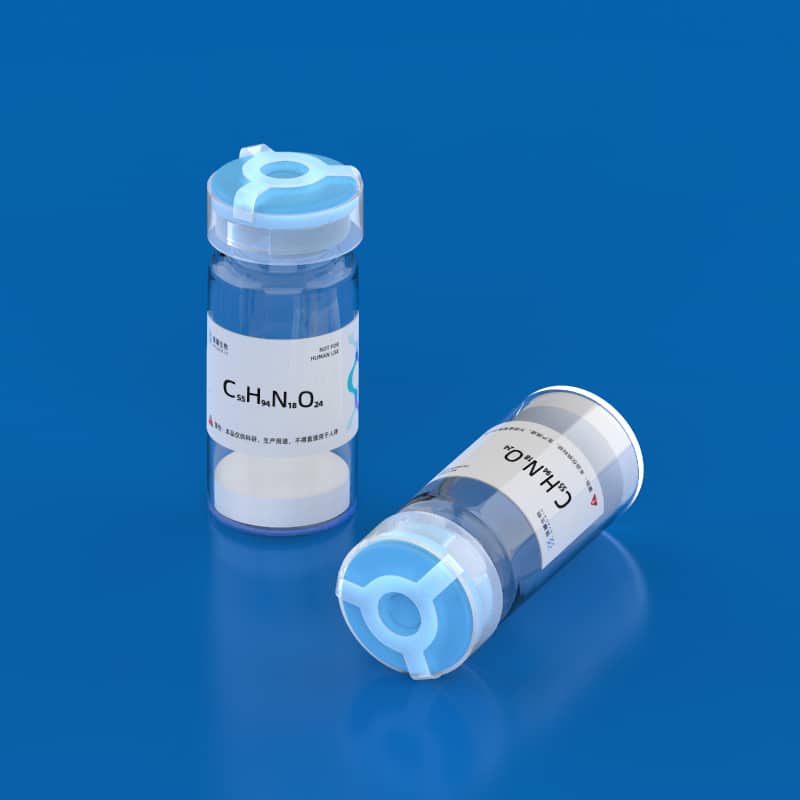
- Name: Pannexin-1 Fragment
- Sequence: VQQKSSLQSESGN
- CAS Number: None
- Formula: C55H94N18O24
- Characteristics: None
- Reference: None
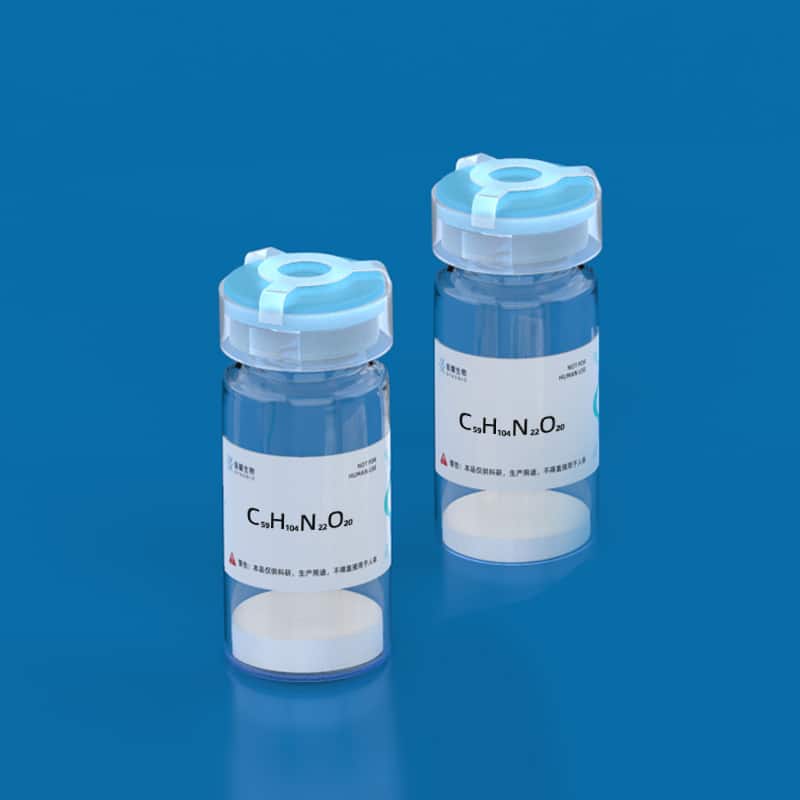
- Name: Pannexin-1 Fragment
- Sequence: EKNSRQRLLNPS
- CAS Number: None
- Formula: C59H104N22O20
- Characteristics: None
- Reference: None
Call Us
+86(021)-50795728
+86(027)-60707970
