Chemokine
Chemokines are a family of small cytokines or signaling proteins that the ability to trigger the migration of cells. Cytokine proteins are classified as chemokines based on structural similarities, such as around 8-10 kDa in mass, and the presence of four cysteine residues in conserved locations, which are essential for forming their 3-dimensional shape. There are four subfamilies of chemokines: CC, CXC, C and CX3C. Each of these proteins interacts with chemokine receptors, which are G protein-linked transmembrane receptors that are specific to the surfaces of their target cells, to exert their biological effects.
Chemokines can direct cell migration, for example, guiding lymphocytes to lymph nodes where they interact with antigen-presenting cells in these tissues to screen for pathogen invasion.
They also promote angiogenesis or guide cells to tissues that provide specific signals critical for cellular maturation. Primarily serving as chemoattractants for leukocytes, inflammatory chemokines recruite monocytes, neutrophils, and other effector cells from the bloodstream to areas of tissue injury or infection. Certain inflammatory chemokines stimulate cells, causing an immune response or promoting wound healing. Many different cell types are able to release them, which are used to direct cells of innate and adaptive immune systems.
Notice: All peptides are only for research purposes, Not for clinical use.
Chemokine
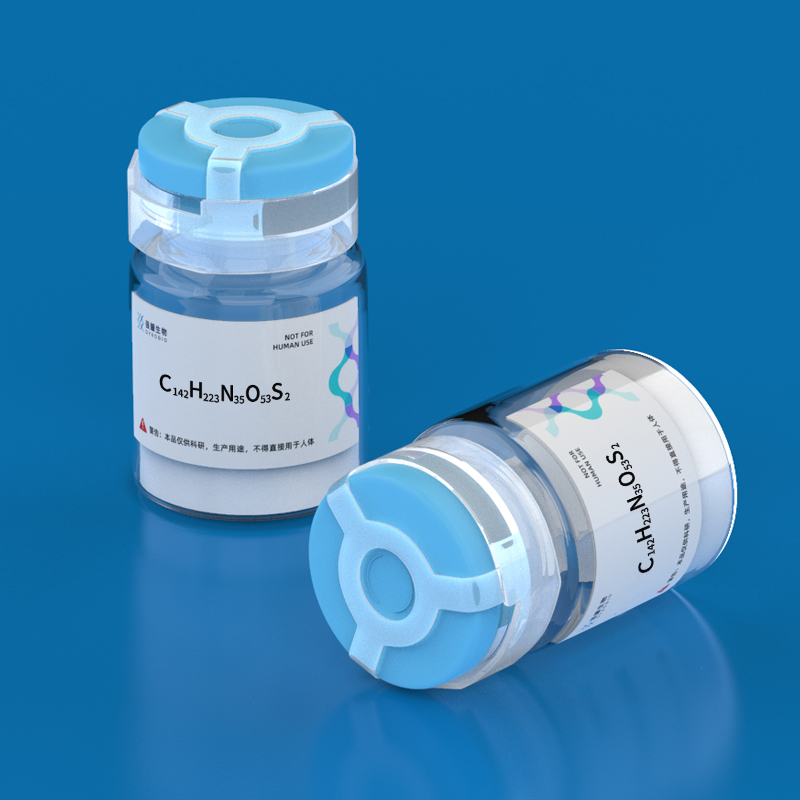
- Name: CC Chemokine Receptor 3 Fragment I, amide
- Sequence: MTTSLDTVETFGTTSYYDDVGLLCEKADTR-NH2
- CAS Number: None
- Formula: C142H223N35O53S2
- Characteristics: None
- Reference: None
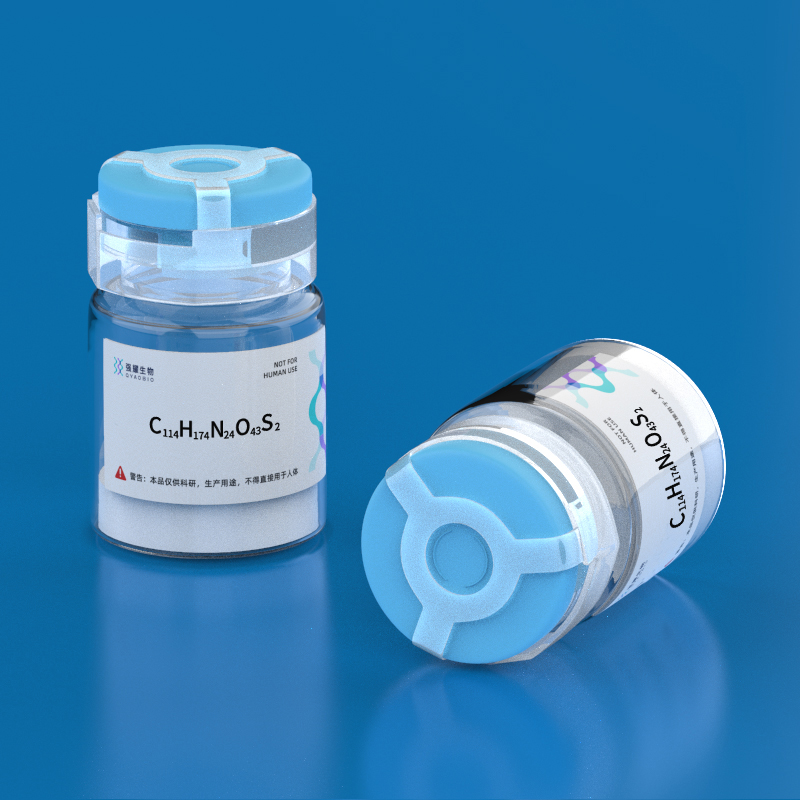
- Name: CC Chemokine Receptor 3 Fragment II
- Sequence: MTTSLDTVETFGTTSYYDDVGLLC
- CAS Number: None
- Formula: C114H174N24O43S2
- Characteristics: None
- Reference: None
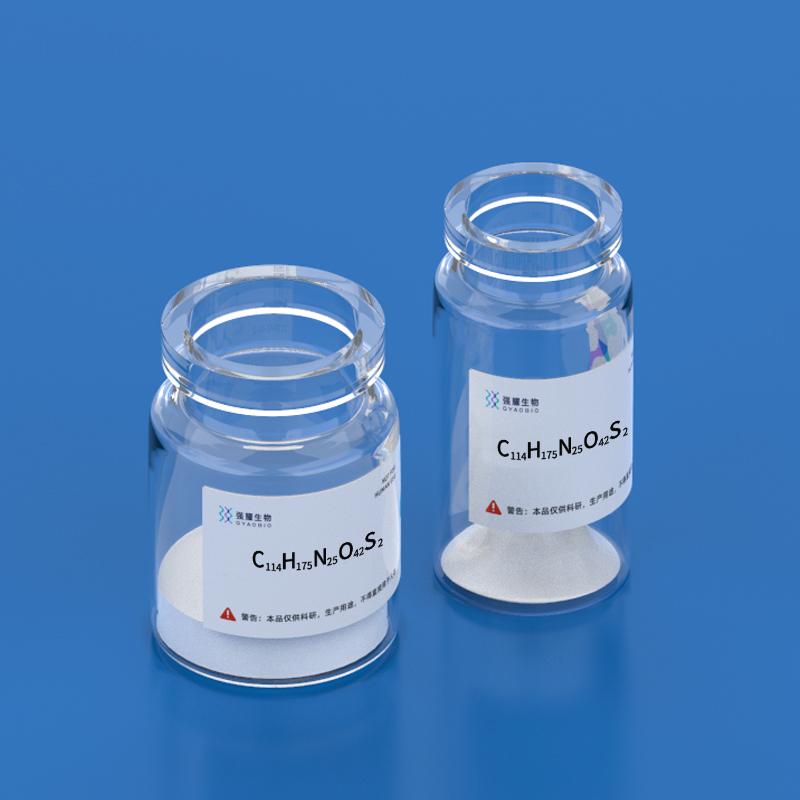

- Name: CC Chemokine Receptor 3 Fragment II, amide
- Sequence: MTTSLDTVETFGTTSYYDDVGLLC-NH2
- CAS Number: None
- Formula: C114H175N25O42S2
- Characteristics: None
- Reference: None
Call Us
+86(021)-50795728
+86(027)-60707970
