Glycosylation of Peptides
Introduction
Glycosylation of peptides is a promising synthesis strategy, it can modulate the physico-chemical properties of peptide drugs, and improve the absorption through biological membranes. There are different synthesis methods of peptide glycoconjugates.
In reason of peptides have high activity, low toxicity, target specificity, minimal non-specific, drug-drug interactions. These substances have therapeutic potential in several disease treatments. However, the poor physico-chemical properties of peptides restrict the efficient delivery. Therefore, chemical modification of peptide are applied to overcome these obstacles.
Chemical modification of peptide glycosylation can attach the glycosyl units to peptides, in order to alter the features, like conformation structures, unique functions, and chemical, physical, biochemical properties. Thus, the impact of peptide glycosylation is an effective strategy for peptide delivery and therapeutic application.
Glycosylation Strategy for Peptide Delivery
The attachment of carbohydrate moieties can improve the bio-availability of peptides, it has the advantages as following:
- Target specific organisms and enhance bio-distributions
- Improve the penetration through biological membranes
- Increase the metabolic stability and reduce the clearance rate
- Increase the receptor-binding
- Protect the amino acids’ side chain from oxidation
- Maintain and stabilize the physical properties, like precipitation, aggregation and thermal and kinetic denaturation
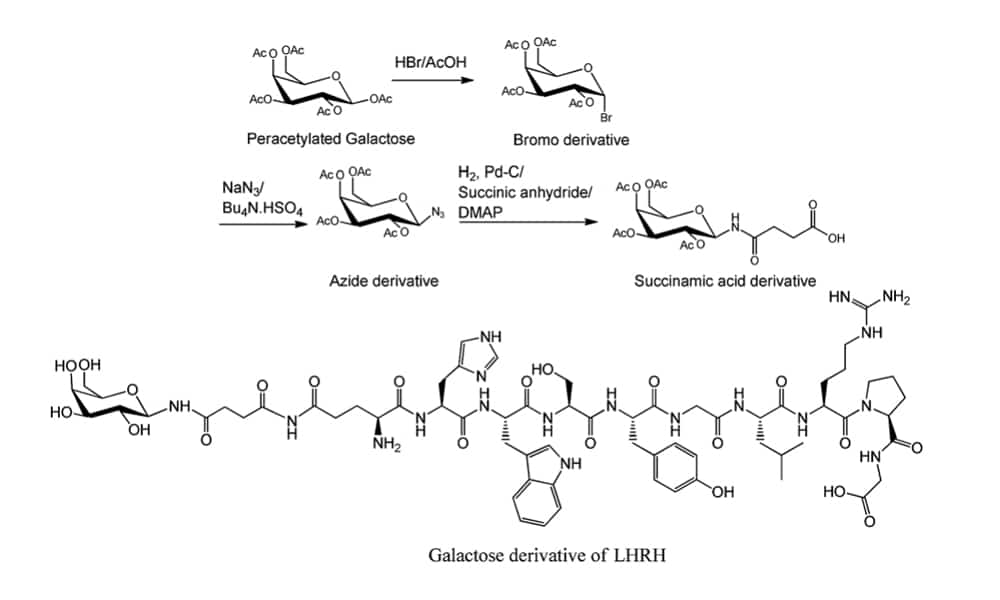
Furthermore, conjugation of sugars and peptides.
Site-specific Glycosylation
N- and O-terminus Glycosylation
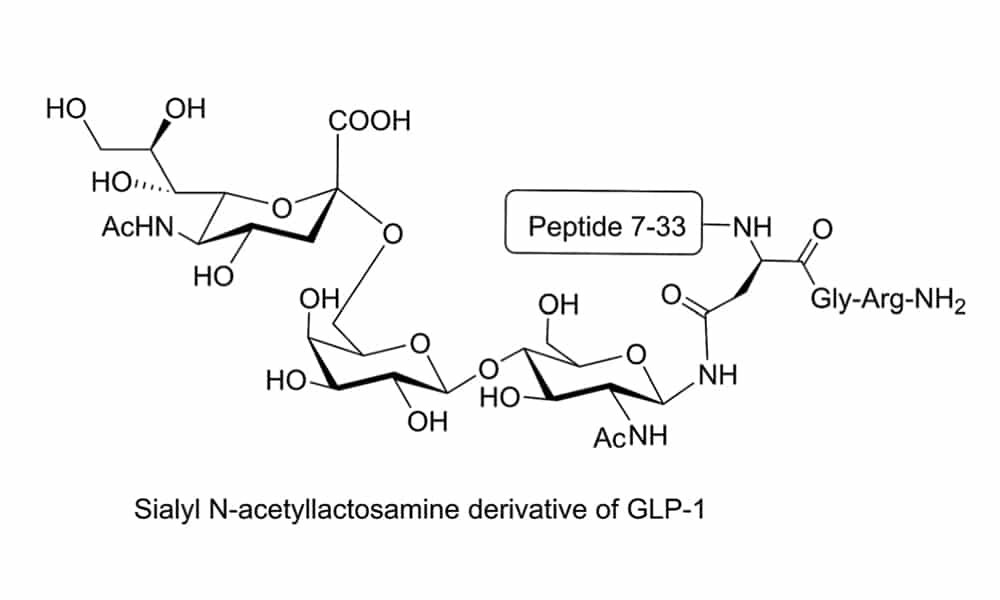
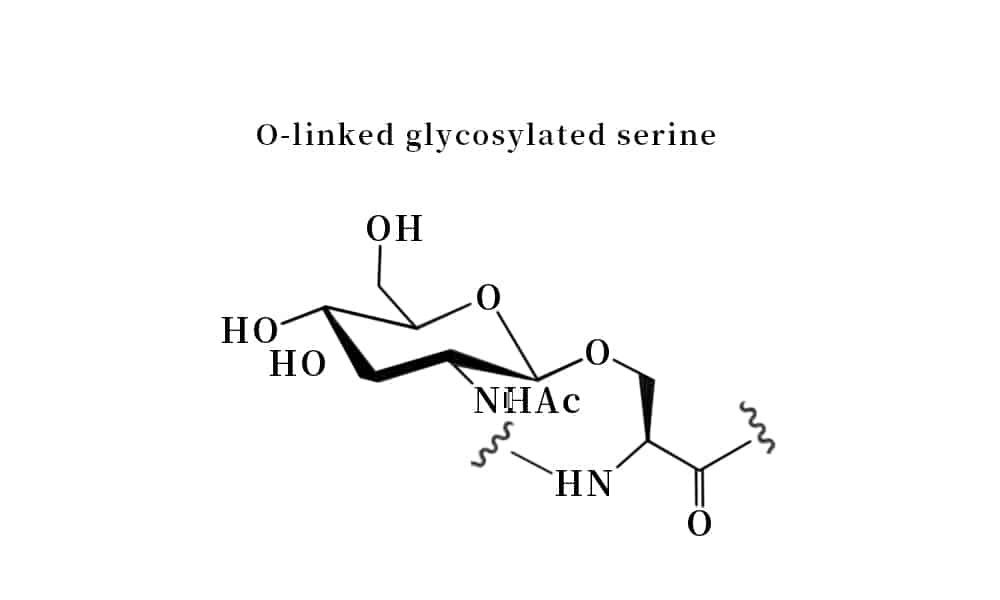
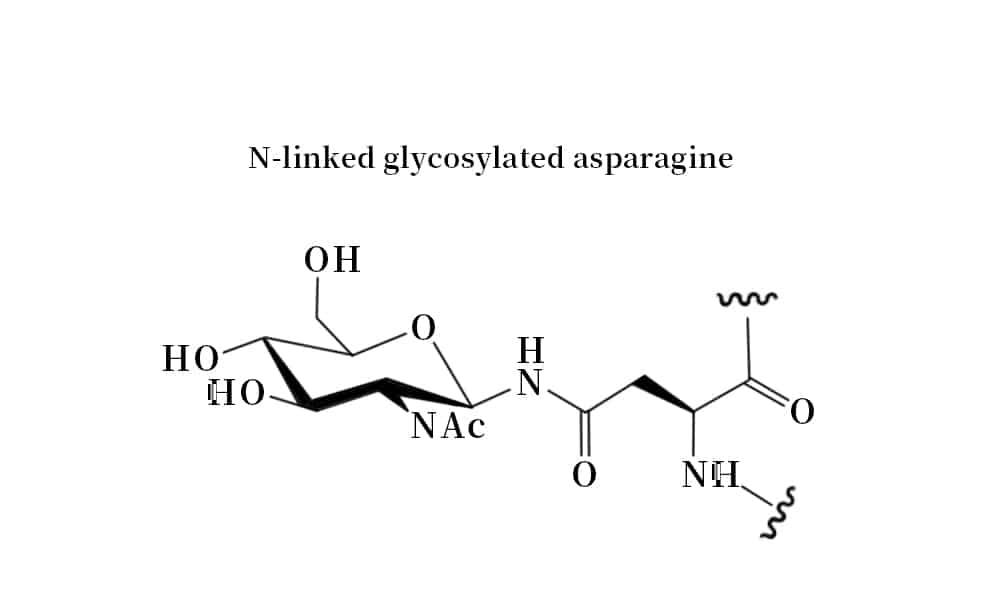
The N- and O- terminus glycosylation of peptides are naturally occurring, these modifications are through co-translational or post-translational. The N-linked glycosylation forms the amide bond through asparagine residue, while the O-linked glycosyplation binds carbohydrate moieties to Ser or Thr residues through ether bonds. Both chemical and chemo-enzymatic methods can synthesize the glycopeptides and glycoproteins.
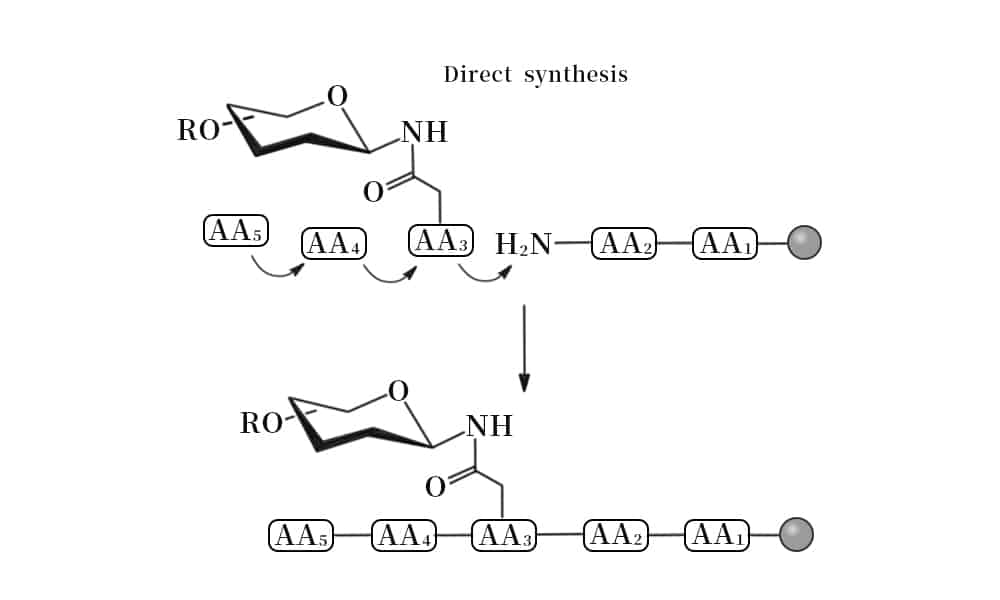
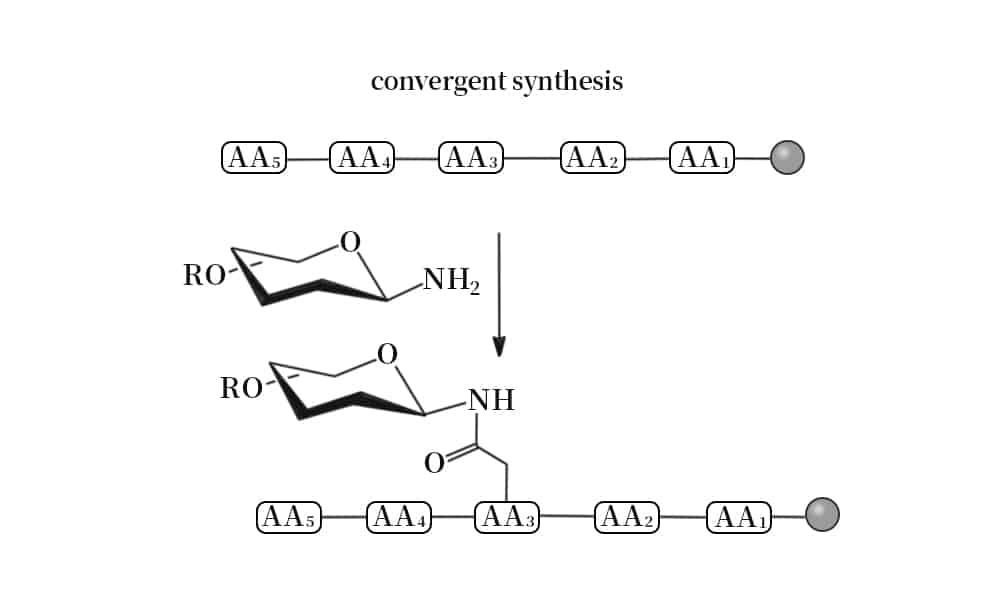
Chemical Glycosylation
There are two common chemical strategies for the synthesis of N- or O- terminus glycopeptides: direct synthesis, convergent synthesis. In direct synthesis method, the pre-glycosylated amino acid is binding to the elongating peptide in solid phase peptide synthesis (SPPS). The fluorenylmethyloxycarbonyl (Fmoc) and tert-butyloxycarbonyl (Boc) are applied in SPPS. However, it is difficult to synthesize long peptide with more than 50 residues by stepwise, because of the incomplete couplings and epimerisation. Therefore, convergent (fragment-condensation) method is the alternative approach to overcome this problem. This method is particularly suitable for N-linked glycopeptide synthesis, while the O-glycosylation is not achievable.
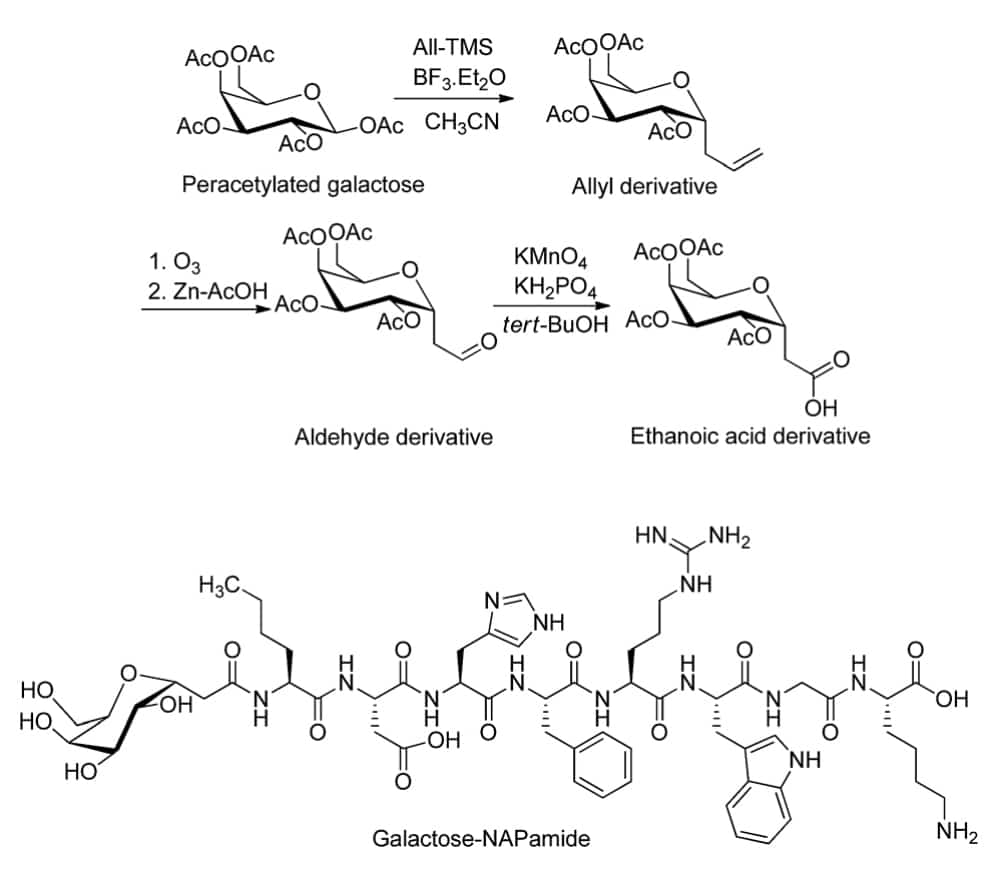
Chemo-enzymatic Glycosylation
Chemo-enzymatic glycosylation is a powerful tool for effective peptide synthesis of complex carbohydrates. It combines the flexibility of chemical synthesis and high stereo-selectivity of enzyme-catalyzed reactions. This technique is the ideal choice for complex chemical synthesis, such as the attachment of oligosaccharide to polypeptides. There are three common enzymes in the chemoenzymatic technology: Endo-β-N-acetylglucosaminidases (ENGases), glycosyltransferases, oligosaccharyltransferases (OST).
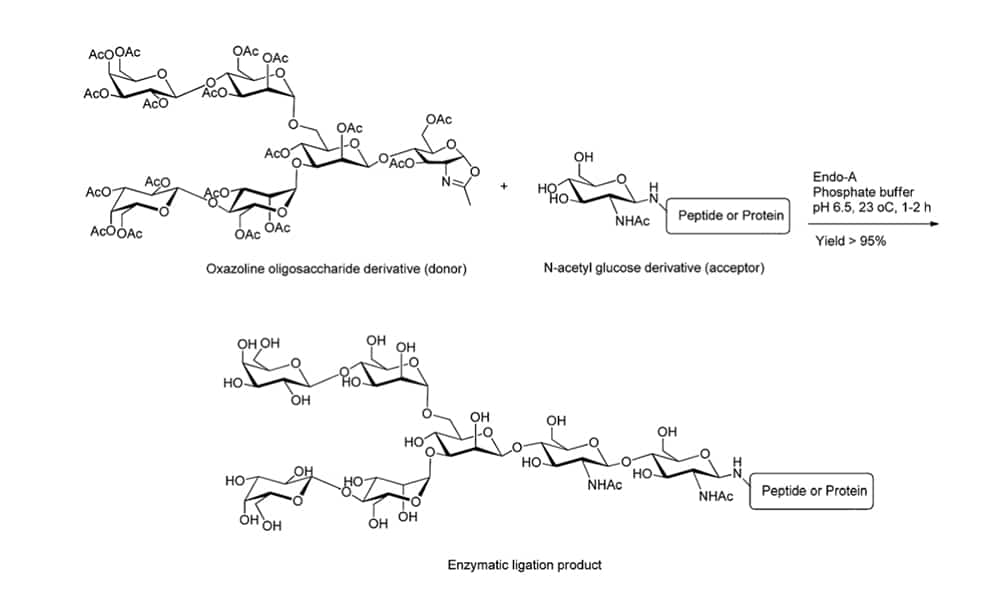
- ENGases can couple the intact oligosaccharide to N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc)-containing peptide or protein in one single step. In addition, ENGases have transglycosylation activity to form the new glycopeptide by attaching the released oligosaccharyl moiety to a suitable acceptor.
- Glycosyltransferases are able to extend the sugar chain by attaching one monosaccharyl residue per time. The glycosyltransferases have high regio-selectivity and stereo-specificity for glycosyl unit attachment without protecting groups.
- Bacteria oligosaccharyltransferases (OST) are the key protein enzymes for N-glycosylation of proteins in bacteria biosynthesis systems.
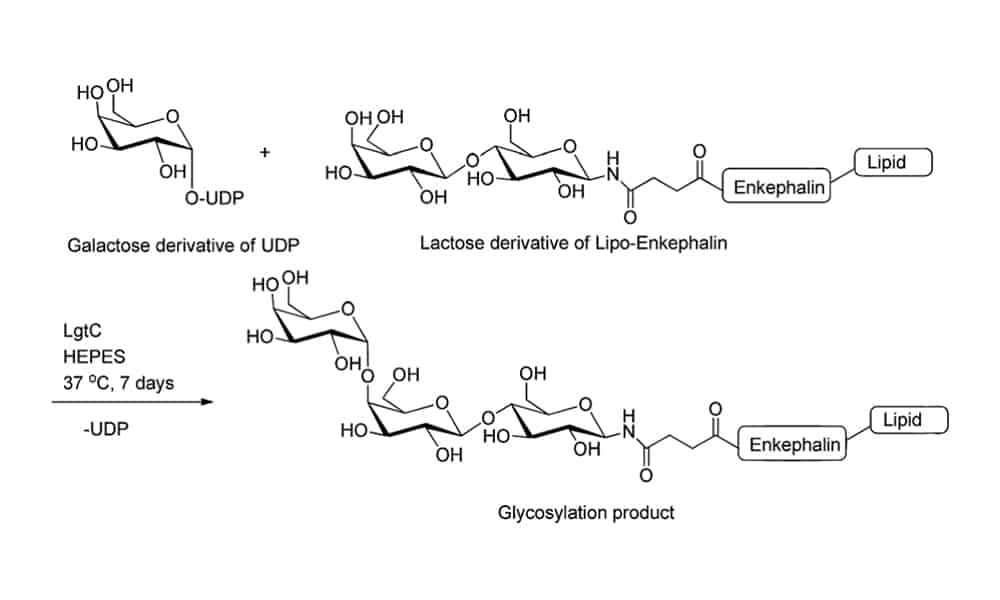
Property Impact of Peptid Glycosylation
The physicochemical properties affect the pharmacokinetic profile and metabolic fate of peptide drugs in human body. Glycosylation can change the conformation of peptide backbone and enhance the molecular stability. The position of glycosyl units in peptide structure is an important factor for the conformation of peptide backbones, this will affect the biological properties of modified peptides.
Pharmacological Characteristics of Peptide
GLycosylation can improve the poor pharmacological properties of peptides and form the therapeutic efficacy of glycopeptides. Since endogenous peptides have typically short half-lives in biological environments. The position of glycosyl units on peptides will affect the biodistribution and pharmacological activity, peptide–receptor interactions.
Comparing to the galactose-modified analogues, the glucosylated and mannosylated vasopressin have higher renal untake, this reduces the peptide clearance from the body. Additionally, the glucosyl and mannosyl conjugates can bind specifically to the kidney microsomal membrane, in order to injection the renal uptake of peptides.
Therapeutic Development of Glycopeptides
Neuropeptide Therapeutics
It is hampered to deliver neuropeptides successfully to the central nervous system for the treatment of neurological disorders. Due to the formidable obstacles like blood brain barrier (BBB), enzymatic digestion and liver clearance. Therefore, glycosylation is approved as the effective strategy to improve brain delivery of therapeutic peptides. This technology can promote the penetration of opioid peptides into the brain and increase the pharmacological activity. The glycosylated neuropeptides have a significant increase in their bioavailability, this enhances the analgesic effect of the glycopeptides.
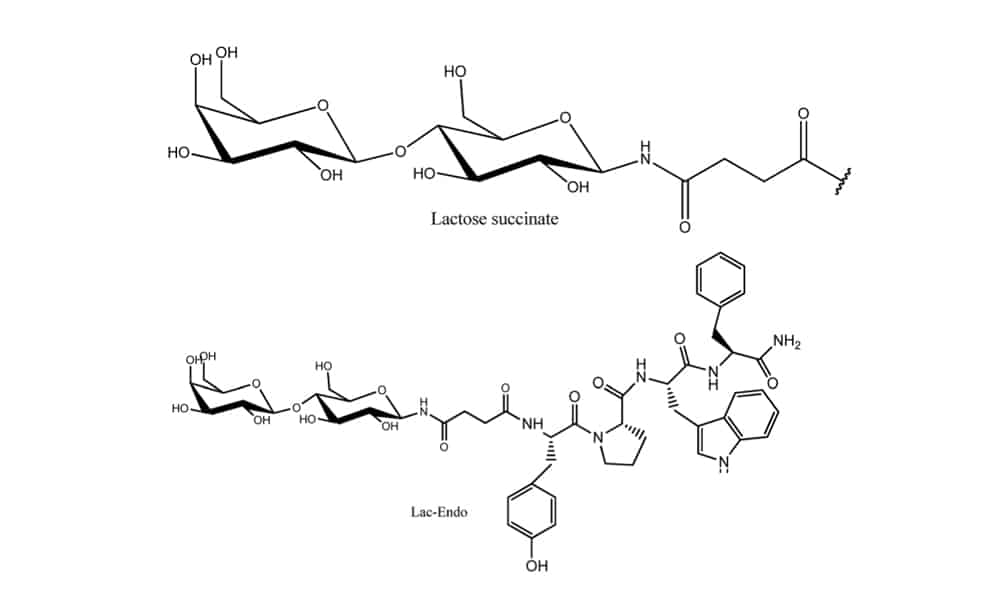
Radio-Pharmaceuticals
Peptide glycosylation is a successful strategy to improve the biodistribution and poor pharmacokinetic profile of radiolabeled peptides in diagnostic and therapeutic process. Conjugation of glucose moiety with radiolabeled bombesin analogues can reduce abdominal accumulation and increase the untake by tumours, never affect the cell internalisation of modified peptides. In addition, the improved biokinetic property of glycosylatied peptide make it widely applied for tumour targeting and angiogenesis imaging.
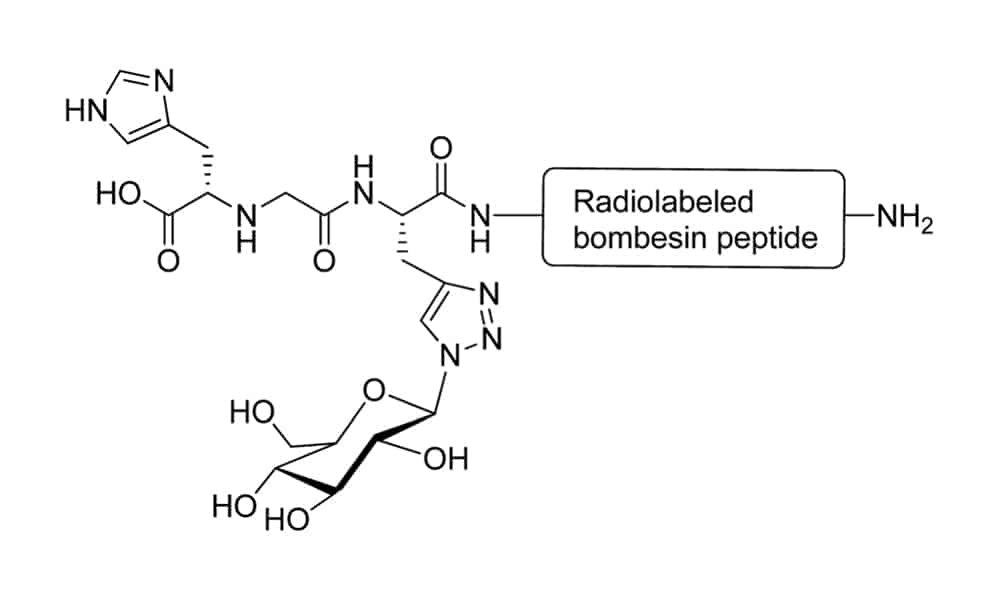
Glyco-targeting Delivery
Glyco-targeting delivery is also known as carbohydrate-mediated delivery, it is a strategy for applying cell surface recognition to target specific organs. Carbohydrates are useful candidates for receptor-targeted peptide delivery, these lectin receptors are expressed in different cell membranes such as liver, kidney and tumour cells. Therefor, liver, kidney and brain targeting is achievable through glycotargeting.
Conclusion
The peptide glycosylation can enhance the therapeutic behaviour of peptide drugs by optimizing the pharmacokineic properties. The development of peptide-based therapeutics requires the optimization of pharmacological profiles. The incorporation of carbohydrate moieties into peptides sequences can change the physicochemical properties, and result in increased membrane permeability and improved proteolytic stability. In order to understand the effect of glycosylation on the pharmacological properties of peptides, we require the rational design of glycopeptides with enhance biological activity.