Lipopeptides and Lipoglycopeptides
Introduction
Lipopeptides and lipoglycopeptides are antibiotic classes with activity against gram-positive bacteria on the bacteria cell wall. Lipopeptides can create the ion-conducting channel, then cause potassium efflux and membrane depolarization, and disrupt the cell membrane finally. In order to inhibit protein synthesis and eventuate bacterial cell death. Lipoglycopeptides have the dual action of binding peptidoglycan precursors and causing cell membrane depolarization, this will inhibit the bacterial cell-wall synthesis.
Daptomycin, telavancin, dalbavancin, and oritavancin belong to this drug group. All these medications are administered IV, as the poor oral absorption. Both two classes of antibiotics are applied as alternative agents for gram-positive infections like bacteremia, skin and soft tissue infections. Telavancin as a novel lipoglycopeptide, is effective against ventilator-associated and hospital-acquired pneumonia.
Lipopeptides
Lipopeptide Chemistry
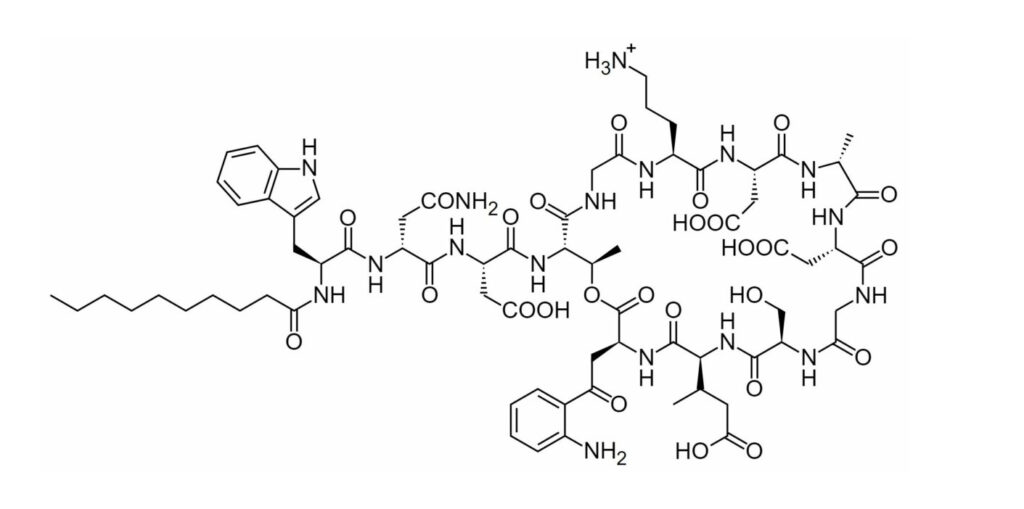
Daptomycin is the only member of lipopeptide class, it is a large molecule with multiple amino acids and decanoic acid. Its chemical structure has 13 amino acids with 10 forming an ester-liked amino acid ring, and the terminal L-tryptophan bond to decanoic acid.
Mechanism of Lipopeptide Activity
The bactericidal activity of lipopeptide is only against the gram-positive bacteria with concentration-dependent killing. The common bacterial mechanism including:
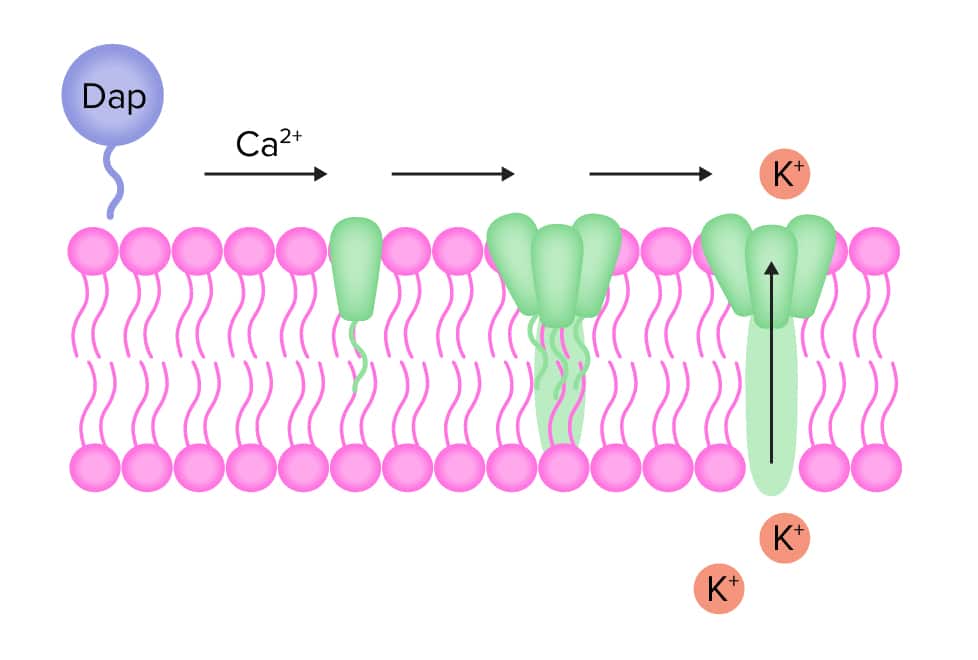
- Bind to bacterial membranes by lipophilic tail (calcium-dependent), then create the hole or channel in membranes, result in potassium ions to leak out.
- Rapid depolarization will result in loss of membrane potential, and inhibit synthesis of proteins, RNAs, and DNAs.
- Initiated process lead to final cell death.
Daptomycin (Dap) can complex with calcium in bactericidal process.
Lipoglycopeptides
Lipoglycopeptide Chemistry
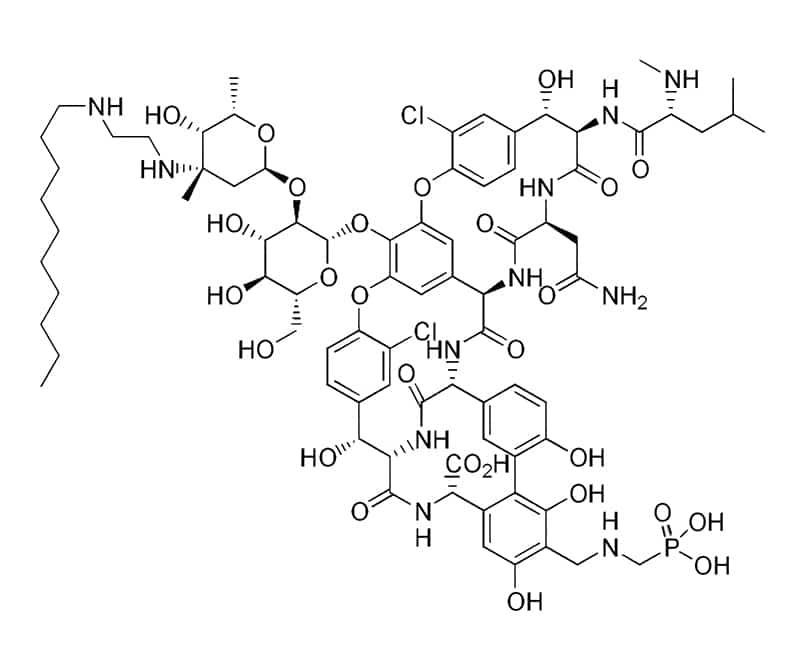
Lipoglycopeptides are semisynthetic derivatives of glycopeptides. These compounds contain the lipophilic side chains with different size attaching to the glycopeptides, in order to prolong the half-life. Lipoglycopeptides also have bactericidal activity against the gram-positive bacteria.
The common lipoglycopeptides including:
- Telavancin: derivative of vancomycin
- Dalbavancin: teicoplanin-like molecule
- Oritavancin
Mechanism of Lipoglycopeptide Activity
Lipoglycopeptides are bacterial with concentration-dependent killing, the mechanism of action for lipoglycopeptides is similar to glycopeptides. However, lipoglycopeptides have dual actions:
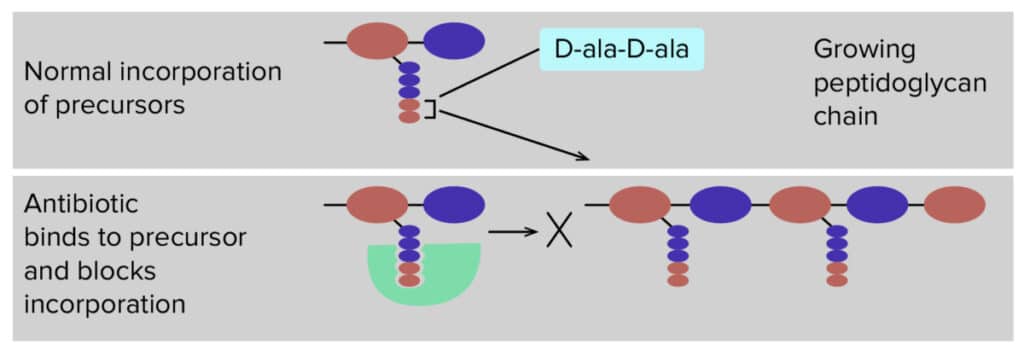
- Bind to D-alanyl-D-alanine terminus of cell-wall peptidoglycan precursors, this is similar to glycopeptides, but with higher potency, then block peptidoglycan polymerization and inhibit cell-wall synthesis.
- Disrupt the bacterial cell membrane, result in depolarization, increased permeability and cell death. This is similar to lipopeptides.
In addition, Oritavancin also can inhibit RNA synthesis.
Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetics of Lipopeptides
Daptomycin Pharmacokinetics
Daptomycin has poor oral absorption, it is toxic to the muscles and only administered IV. It has a serum half-life of 8–9 hours.
Daptomycin are highly protein-bound with different organ pharmacokinetics:
- Excellent skin and soft tissue penetration.
- It is an option for complicated urinary tract infections, as it excreted in the urine.
- Daptomycin is not useful for pneumonia, since it is inactivated by pulmonary surfactant.
- It has poor penetration of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) even with inflammation in center nerve system (CNS).

Pharmacokinetics of Lipoglycopeptides
Telavancin Pharmacokinetics
Telavancin is not absorbed orally, it has high protein-binding. The serum half-life is 7–8 hours. Telavancin has adequate concentration in skin, soft tissue and lung tissue, thus it is applied in pneumonia, skin and soft tissue infections.

Dalbavancin Pharmacokinetics
Dalbavancin is not oral absorption, it has long half-life with 1- or 2-dose regimen. Dalbavancin has good penetration of skin and bone tissues, but poor CFS penetration. It is eliminated unchanged in the urine.
Oritavancin Pharmacokinetics
Oritavancin is not orally absorbed, it has long half-life for single dose treatment. Oritavancin has no hepatic metabolism, it is excreted slowly in the urine.
Treatment Indication
Lipopeptides and lipoglycopeptides are both active agents against gram-positive bacteria.
Lipopeptides-Daptomycin (IV)
Infection treatment of gram-positive bacteria with intolerance to standard therapy or antibiotic resistance, including: staphylococcus aureus bacteremia (bloodstream infections), complicated skin and soft tissue infections (SSTIs).
Lipoglycopeptides-Telavancin (IV)
Telavancin is an alternative agent for complicated SSTIs, including MRSA and VSE. It is also an effective treatment of hospital-acquired and ventilator-associated pneumonia.
Lipoglycopeptides-Dalbavancin (IV)
Dalbavancin is applied for acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections by gram-positive bacteria.
Lipoglycopeptides-Oritavancin (IV)
Oritavancin is efficient for gram-positive pathogens, including MRSA and VSE.
Comparison of Antibiotics
The following antibiotics are different agents with activity against gram-positive bacteria, all these antibiotics have varying mechanisms on the cell membrane walls.
| Class of Antibiotics | Action Mechanism | Drugs |
| Lipopeptides | Disrupt the bacterial cell membrane by generation of ion-conducting channelsDepolarize the membraneLead to cell death | Daptomycin |
| Glycopeptides | Bind the D-alanyl-D-alanine terminus of cell wall peptidoglycan (PG) precursors to inhibit cell wall synthesis | Vancomycin Teicoplanin |
| Lipoglycopeptides | Dual action in inhibition of cell wall synthesis and depolarization of cell membranes. | Telavancin Dalbavancin Oritavancin |
Conclusion
Lipopeptides and lipoglycopeptides both provide highly bactericidal efficiency, as the increasing resistance in gram-positive organisms. In order to achieve more and more information of possible drug interactions, various lipopeptides and lipoglycopeptides are required in medical and biological researches. Contact Qyaobio for your novel synthesis of lipopeptides and lipoglycopeptides in researches.