Peptide Conjugation
Peptide conjugation can design and manufacture different linkages.
QYAOBIO has extensive expertise in peptide conjugation with different entities, in order to support peptide drug discovery for different purposes. The chemo-selective conjugation entities including: proteins, mono antibodies(mAbs), lipids, small molecules, fluorescent labels, tags.
Peptide conjugates can be designed and manufactured by a wide variety of linkages, such as: thiol-thiol, thioether, oximes, amine-thiol crosslinks, triazoles, and hydrazides. Peptide drug conjugate can improve pharma-cokinetic profiles, modify carriers for targeting and imaging.
Peptide Conjugation Classification
Lipids and PEGs Conjugation
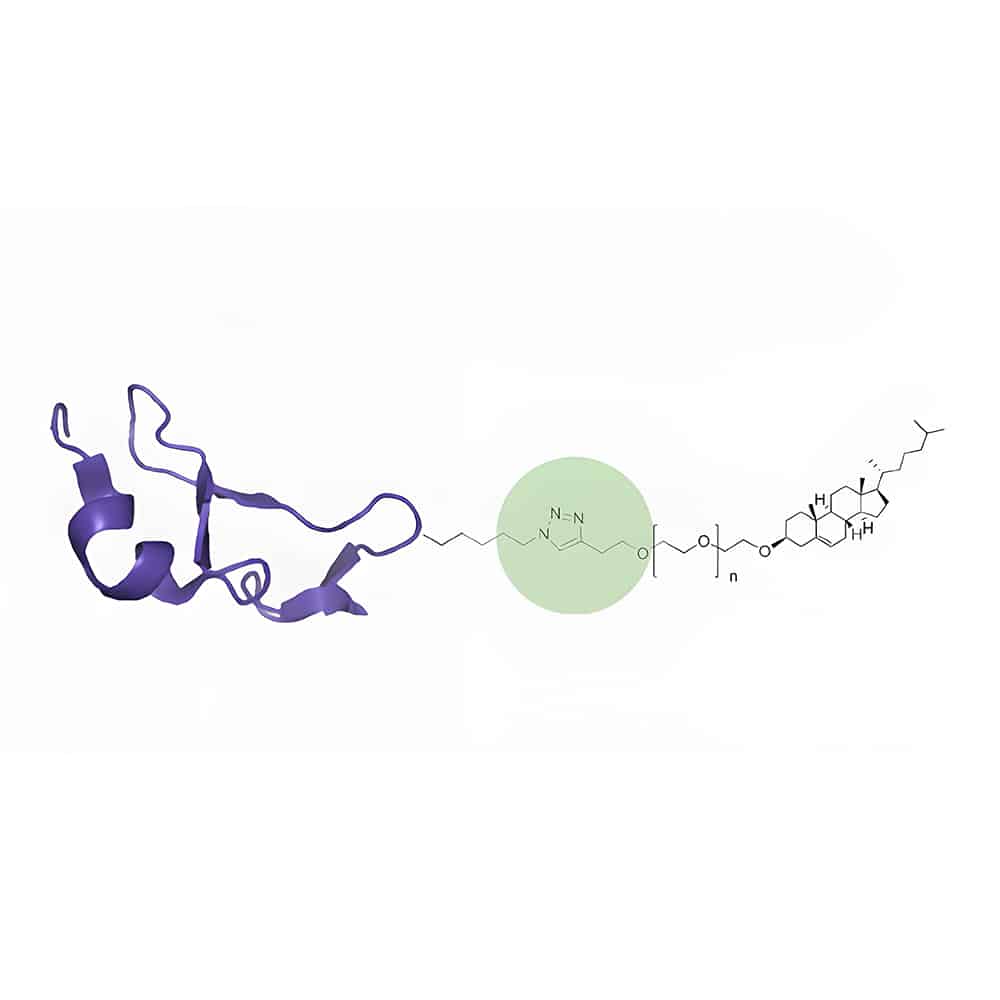
Peptide conjugation with lipids and PEGs are the two common methods to enhance pharma-cokinetics(PK) of peptide drugs. The conjugation of peptides with either fattry aids or cholesterol can promote the binding of peptide drugs to plasma proteins, then improve PK properties. Alternatively, the PK properties of peptides are also optimized by increasing molecular weight of PEGs conjugation, in order to reduce renal filtration and protect against proteolytic degradation.
Proteins and Mono-antibodies Conjugation
Conjugation of proteins or peptides with other peptides, small molecules can be applied for various purpose in pharmaceutical research and study. Such as: antigenic immune response, cellular uptake, receptor medicated drug delivery. The preferred method for peptide-protein linkage is maleimide chemistry, this conjugation is formed through the side chain thiol of cysteine residues. In addition, bromoacetylation or vynilsulfone are also applied for site-specific derivatization.
Small Molecules Conjugation
Peptide conjugation with small molecules like fluorophores, chelating agents and therapeutics result in specific purpose in peptide research and study. QYAOBIO team has extensive experience on the orthogonal and chemo-selective conjugation of synthetic peptides. Such as fluorescent marker of AlexaFluor®, Cy3, FITC, Biotin, imaging agent precursors of DOTA, NOTA.
Protein-peptide Conjugation
As naked peptide antigens are too small to generate significant immune response, peptides should conjugate to large carrier proteins. In order to ensure the effective and successful generation of anti-peptide antibodies.
Peptide-carrier protein coupling
Carrier protein selection
QYAOBIO provides a wide range of carrier protein options for custom peptide conjugations. The most common carrier proteins are the following:
- KLH (Keyhole Limpet Hemocyanin) is the most common carrier protein with molecular weight of 4.5×10⁵ – 1.3×10⁷ Da. Comparing to other coupling proteins, it has higher immunogenicity. KLH-conjugated peptides have limited solubility in water, this give rise to a cloudy appearance. However, the turbidity never affects its immunogenicity, the resulting solution is successful for immunizations.
- BSA (Bovine Serum Albumin) is the most stable and soluble albumins, it contains 59 lysines, while 30-35 are accessible for conjugation. The molecular weight of BSA is 67×10³ Da, it is a popular carrier protein for weakly antigenic compounds.
- OVA (Ovalbumin) is a protein isolated from chicken eggs with MW of 4.5×10⁴ Da. It normally applied as the control carrier protein, in order to verify that antibodies are specific for target peptides, rather than the carrier proteins.
Peptide Design&Synthesis
According to the chemical linkage, peptide-protein conjugation requires synthetic peptides with chemical handles at the specific position. Ensure the peptides get optimally exposed at the surface of protein carriers. In addition, we also can introduce the rigid or flexible space to fine-tune the distance to carrier surface.
Linkage Chemistry
There are two different linkage chemistry for peptide-protein conjugation. Standard Maleimide-based Technology, Advance Hydralink Technology.
- Standard Maleimide-based Technology: The classical linker can connect the protein via the standard amide-bond formation to any free amine group (including: free lysine side chain, N-terminus). Whereas peptides connect to the linker by conjugating to proteins with addition of free thiol to maleimide functionality. This gives to chemically stable peptide-protein linkage, which is unable to destroy under standard laboratory conditions. There are different linkers in format of size, rigidity, and water-solubility.
- Advance Hydralink Technology: Hydralink technology can couple peptides with free aminoxy (RO-NH2) or hydrazino-nicotinamide(HyNic) groups to any desirable carrier protein. Therefor, the carrier proteins are derivatized with the reagent of S-4FB or Sulfo-S-4FB, in order to converts the free amino groups at the protein surface into the benzaldehyde groups. Which can react with the aminoxy or HyNic groups on peptides. Comparing to the standard thiol-maleimide chemistry, this technology can be quantified by UV-spectroscopy at 354 nm. Moreover, this Hydralink chemistry keep dissulfide bonds completely intact, this avoids SS-bond scrambling in free thiol conditions.
Custom Peptide Conjugation
Regardless the common peptide conjugation manufacturing, Qyaobio also provides convenient custom peptide conjugation service for different projects, including: immune response activation, higher stability and cell penetration. Our custom peptide conjugation apply different combination groups like, antibodies, proteins, oligonucleotides, nanoparticles, etc.
Peptide-Protein Conjugation
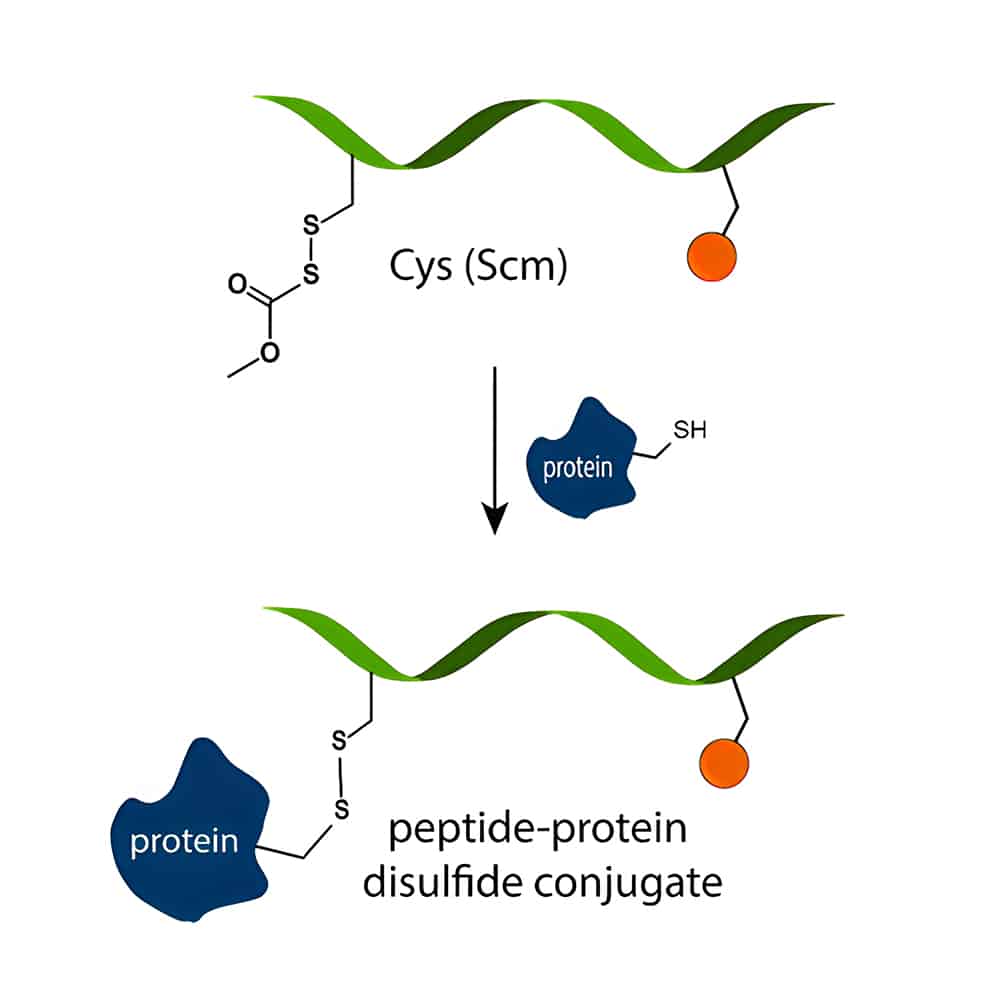
Peptide-protein conjugation induce the B-cell response to the entire immunogen, this new synthetic peptides provide promise as vaccines. As standard peptides with 15–20 AAs are too small to elicit immune response, it is necessary to conjugate peptides to larger carrier proteins.
PEG-Peptide Conjugation
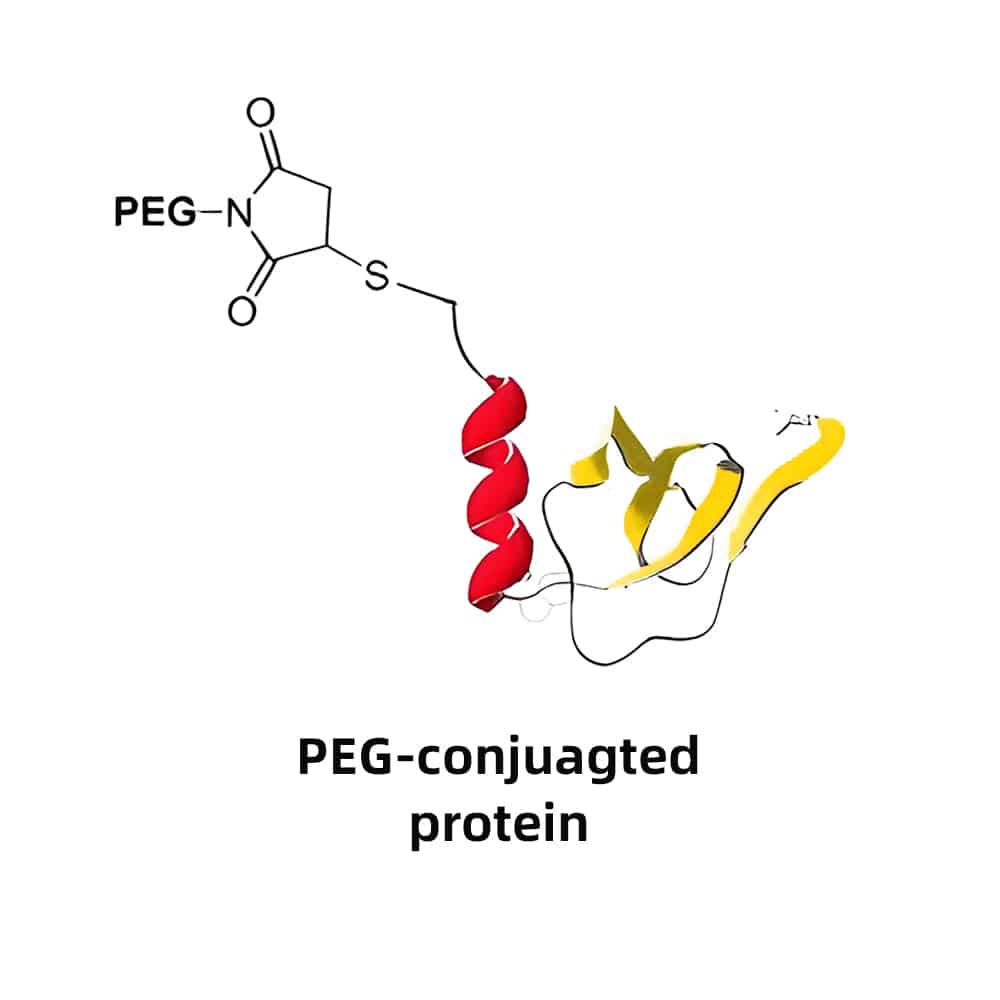
PEG peptide conjugation increase the molecular weight of final PEG-peptides, in order to reduce renal filtration and protect against proteolytic degradation. PEGs have multiple forms and sizes for multiple functions, results in specific properties for various requirements.
Lipid-Peptide Conjugation
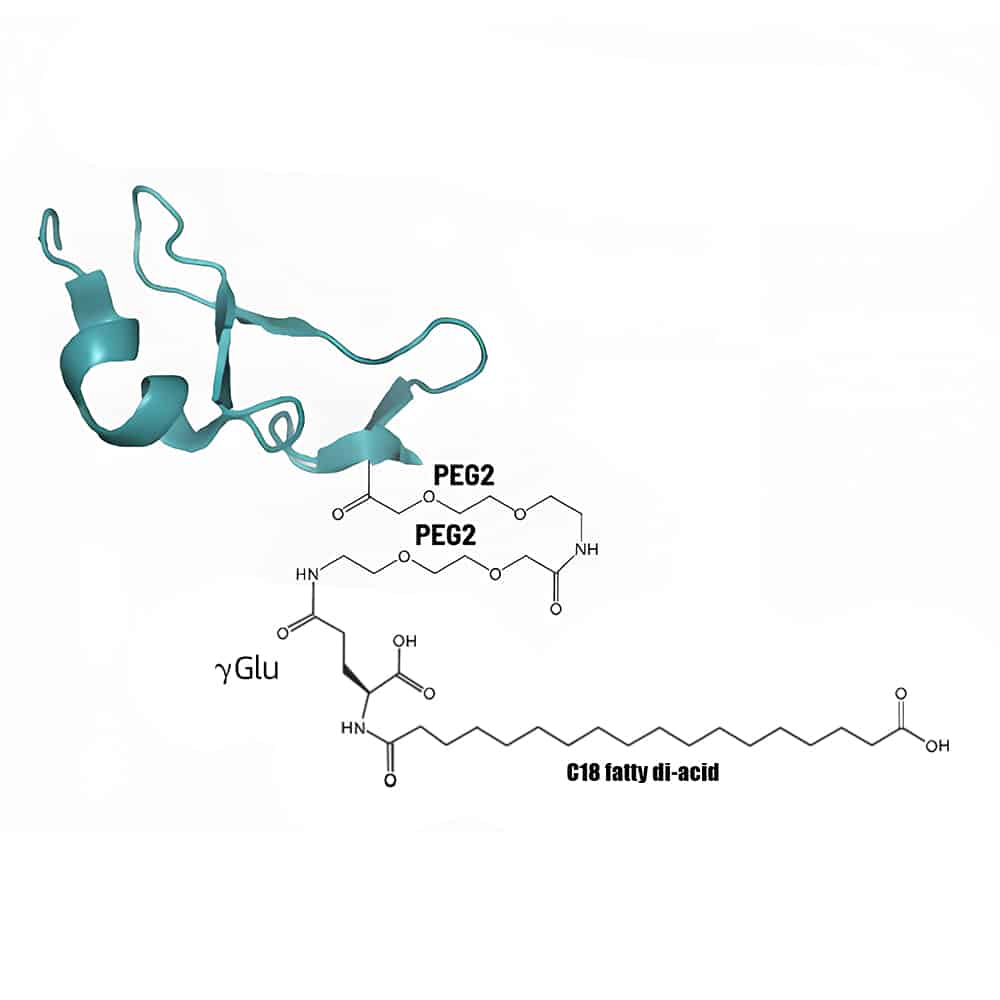
Lipid-peptide conjugation is an effective method to improve peptide pharmacokinetics. It is achieved by lipidation of the main structure or contralateral chain group of the polypeptide. The main fatty acid in lipid-peptide conjugation are caprylic acid (C8), capric acid (C10), lauric acid (C12), myristic acid (C14), palmitic acid (C16) or stearic acid (C18) etc.
Antibody-Peptide Conjugation
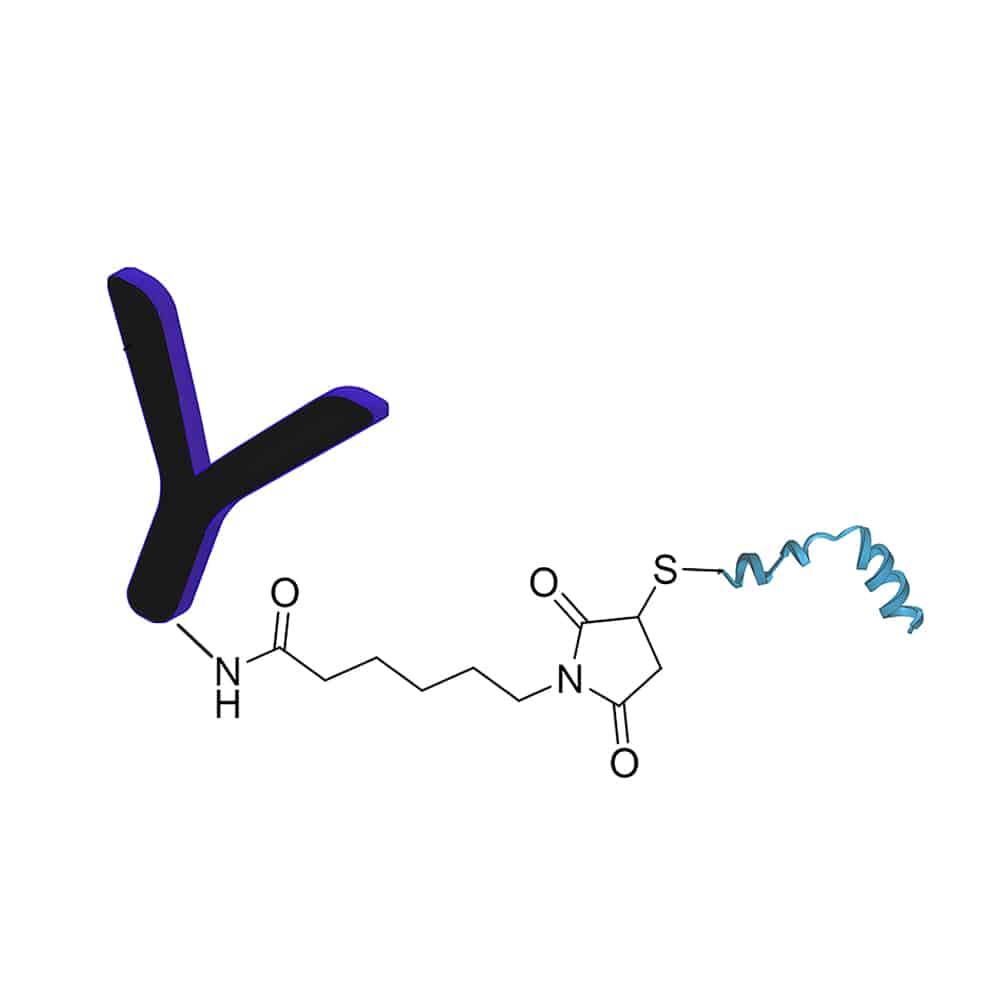
Antibody-peptide conjugates contains an antibody portion and peptides, where the antibody is conjugated to the peptide at specific locations: N-terminal amino acid residue; C-terminal amino acid residue; or lysine residue between the N-terminal and C-terminal. Antibody-peptide conjugation can improve the accuracy of peptide delivery based on the guidance of antibodies. In order to facilitate the delivery of peptide conjugates across the blond-brain barrier.
Peptide-small molecule Conjugation
Peptides are able to couple with different small molecules, like fluorophores, chelating agents, and therapeutics. Peptide-small molecule conjugates have good selectivity, low immunogenicity, good bio-compatibility, strong permeability, and easy excretion. These conjugates are applied widely in tumor-targeted molecular diagnosis.
Peptide-Metal Chelates Conjugation
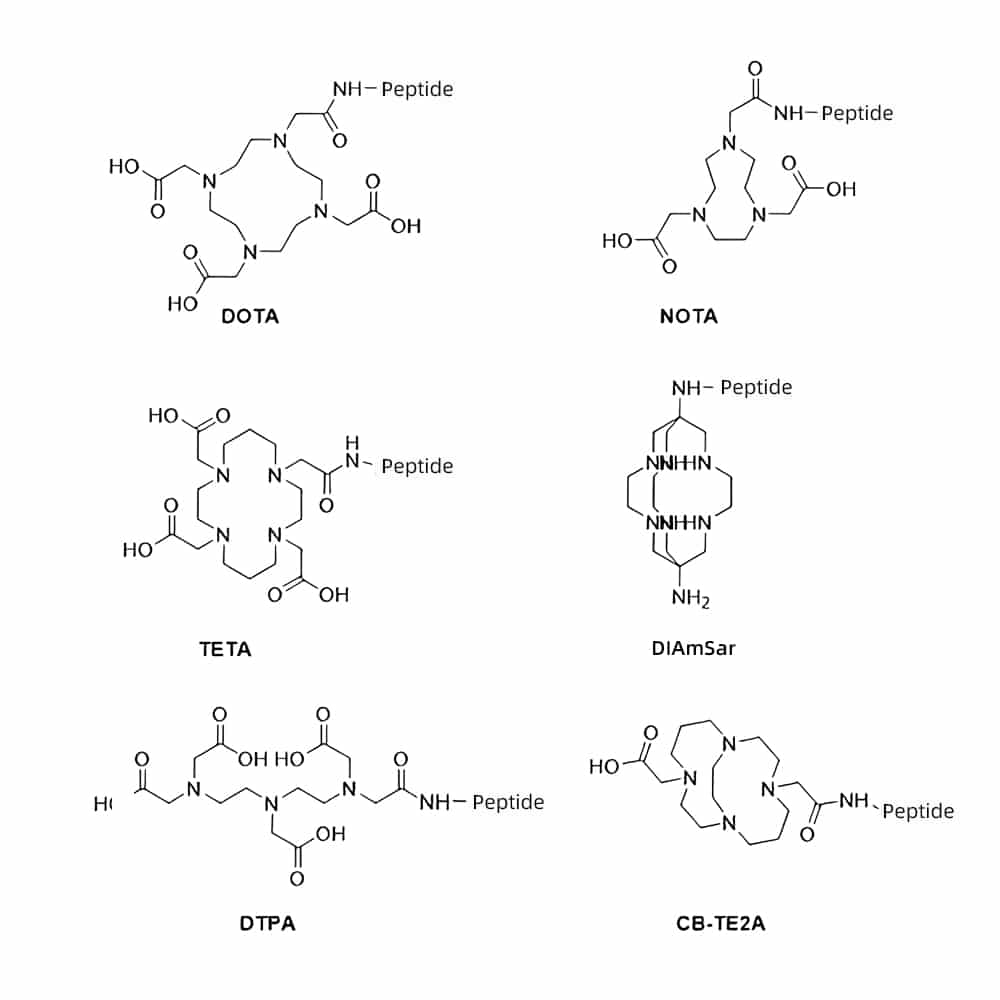
Peptide-Metal Chelates conjugates are compounds with cyclic structure by chelation reaction between peptide and metal ions. These conjugates can improve the bio-availability of metal ions by peptides’ absorption mechanism in the body. Then provide physiological and biochemical characteristics for inorganic metal ions. Peptide-Metal Chelates Conjugation not only promote absorption of metal ions, but also have bio-activities of antioxidant, antibacterial.
DNA-Peptide Conjugation
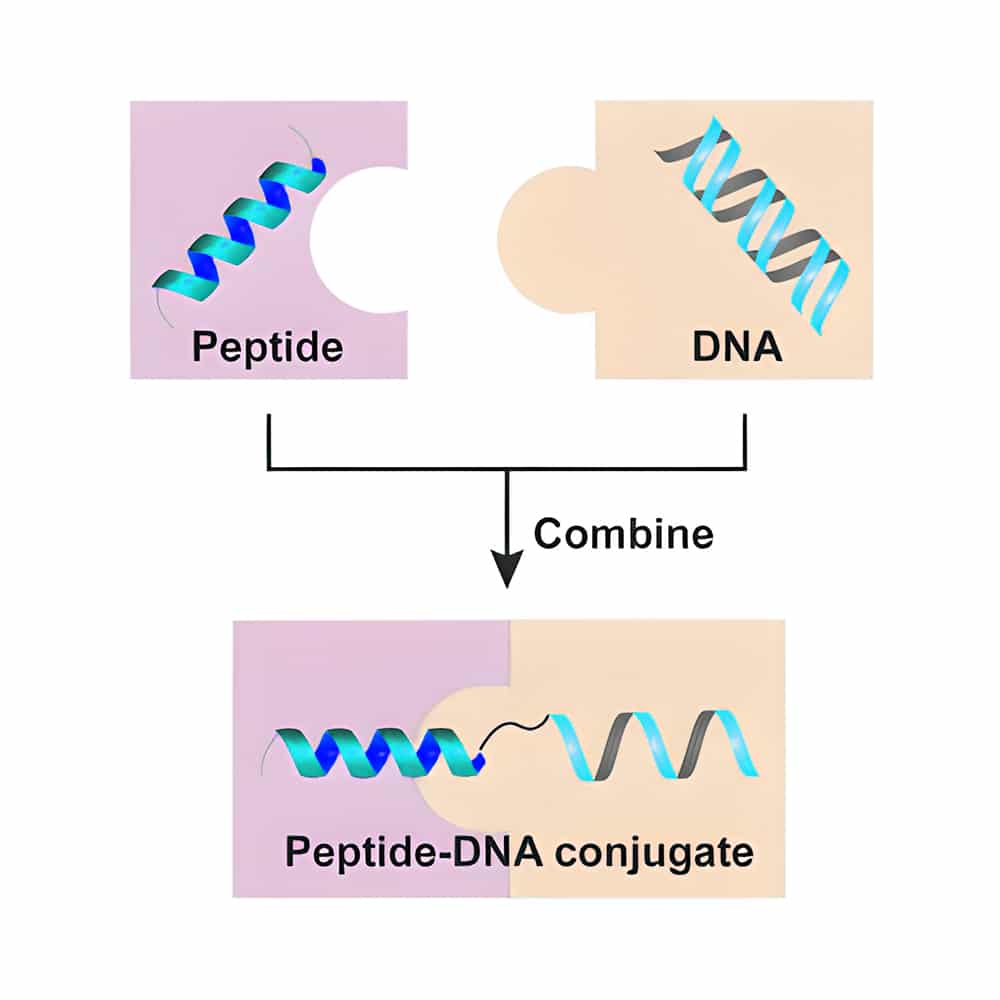
DNA-peptide conjugates are molecular chimeras with nucleic acid moieties and polypeptides, which are applied widely in therapy and nanotechnology. The common DNA-peptide conjugation strategy is combining cell-penetrating peptides with phosphorosulfate DNA chains to enhance the nuclease attack ability. Qyaobio provides customized synthesis and joining of peptides and DNA oligomers. DNA couple with peptides through functionalized phosphoramidite monomers, the most common reactive moieties include amines, thiols, alkoxyamine or hydrazines, aldehydes, azides/alkynes (click chemistry).
RNA-Peptide Conjugation
RNA-peptide conjugate is a useful drug due to its higher stability than RNA. The common synthesis method for RNA-peptide conjugation are:
- Post-synthesis coupling method
- Fully stepwise synthesis method
- Natural coupling method
- Template orientation coupling method
Call Us
+86(021)-50795728
+86(027)-60707970
