Peptide Library
Peptide libraries are applied for target screening in different research area.
Peptide libraries are systematic combinations of a great number of peptides, which are applied widely for target screening in different research area, such as immuno-therapy, vaccine development, drug discovery and proteomics. QYAOBIO provides comprehensive peptide library service with extensive QC service to ensure your study success, including TFA removal, solubility testing, endotoxin control & analysis.
Peptide library is the tool for protein studying and researching, it contains a great number of peptides with a systematic combination of amino acids. The most common synthesis method of peptide library is solid phase peptide synthesis. As the peptide library is synthesized on resin mostly, which can be make as flat surface or beads.
Classifications of Peptide Libraries
The peptide library provides a powerful tool for drug design, protein-protein interactions, biochemical and pharmaceutical researches. Synthetic peptide libraries are synthesized without utilization of phage or other biological systems.
According to the distinguishing characteristics of synthesis method in each peptide library, there are at least six subtypes of peptide libraries:
Overlapping peptide library
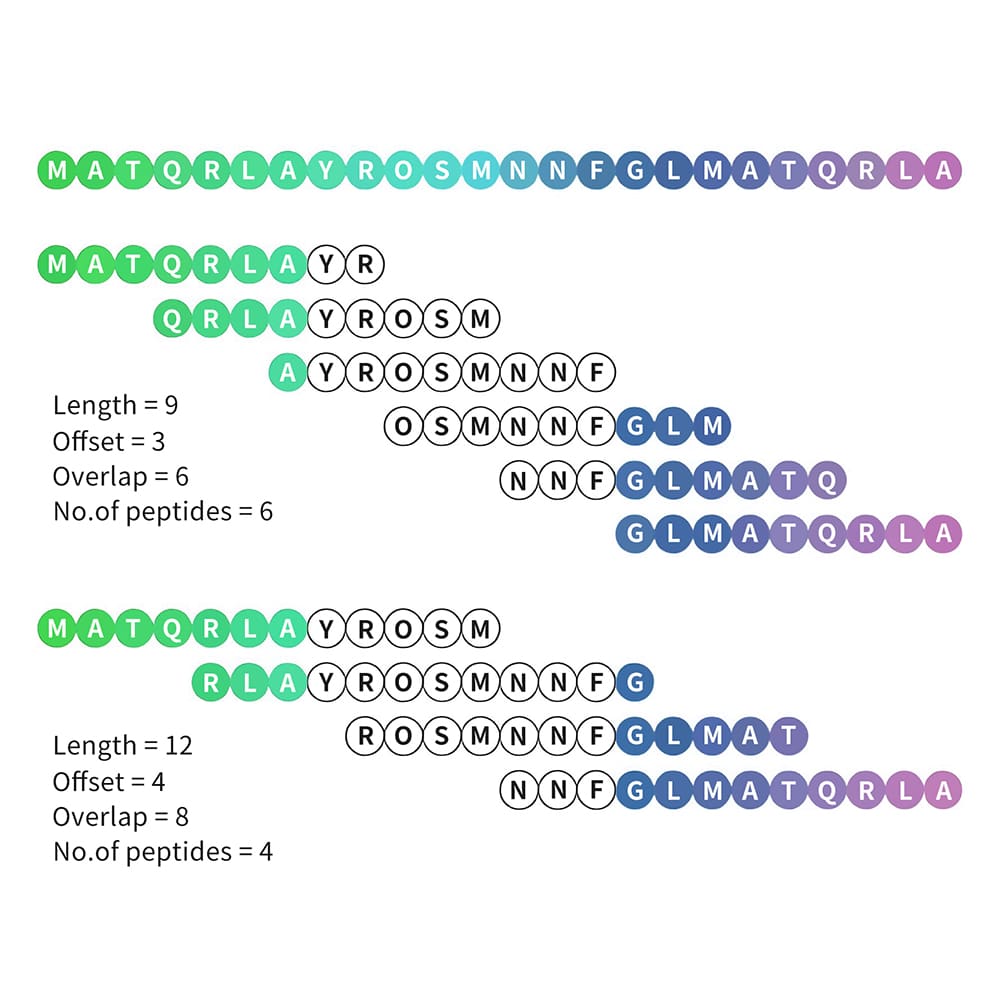
Overlapping peptide library is applied in epitope mapping. This peptide library generation process is defined by two parameters: peptide length and offset number. The offset number reflects the overlapping degrees. Therefore, careful selection of these two parameters are critical to achieve optimal balance between data value and experiment cost. Normally, shorter peptides are easier to synthesize but fewer chances for multiple epitope hits. Greater degree of overlapping (small offset number) results in more change in multiple epitope hitting. Both above case will increase the synthesis number for the peptide library.
Truncation peptide library
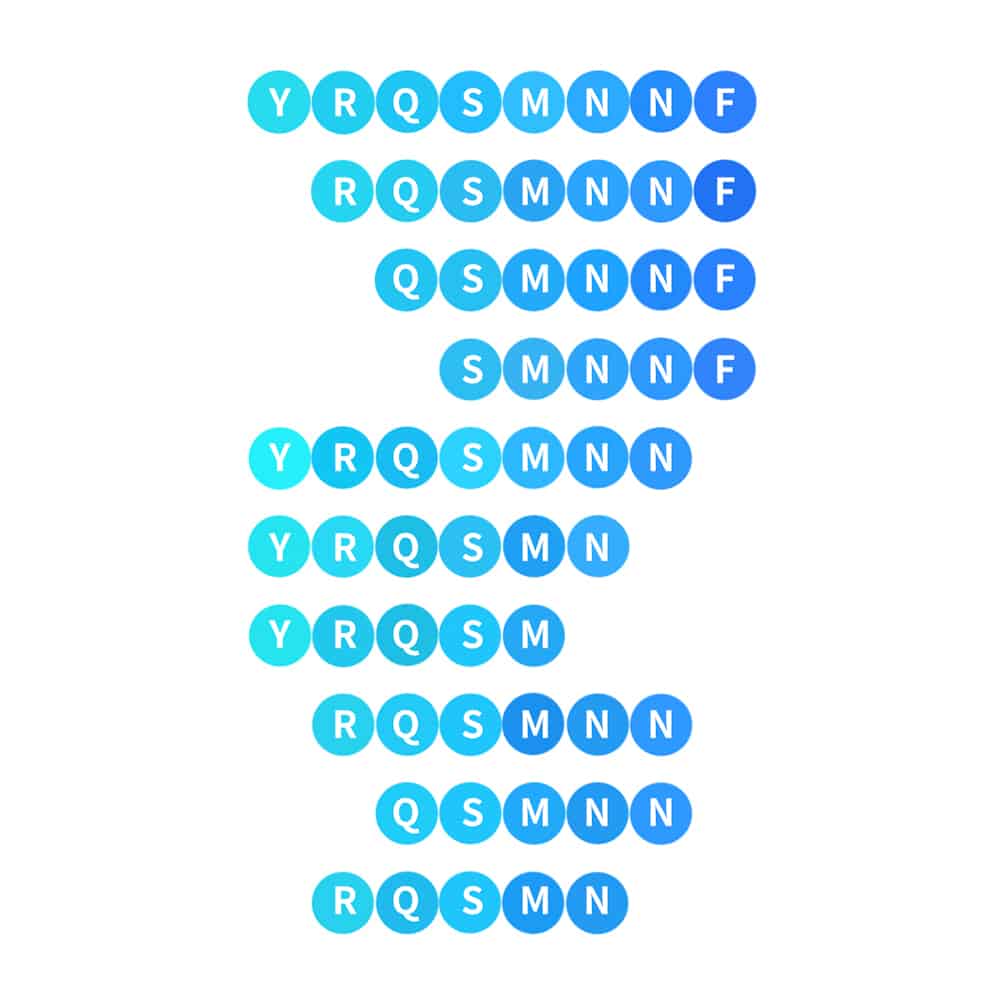
Truncation peptide library can identify the shortest amino acid sequence for the peptide activity. The truncation process is a systematic reduction of resides from each flank of the original peptide. The construction of truncation library can be centred around the key amino acid residues with knowledge in Alanine Scanning Library.
Random Peptide library

Random library are used in sequence optimization, this is similar to positional scanning library. This library is constructed by random substitution of selected positions on the original peptide, and simultaneous injection with other natural amino acids in shot gun’s approach. In order to elucidate potential alternatives for enhanced peptide activity. The random library is the indispensable tool for sequence optimization, it can generate alternative peptides with potential enhanced activity.
Alanine scanning library
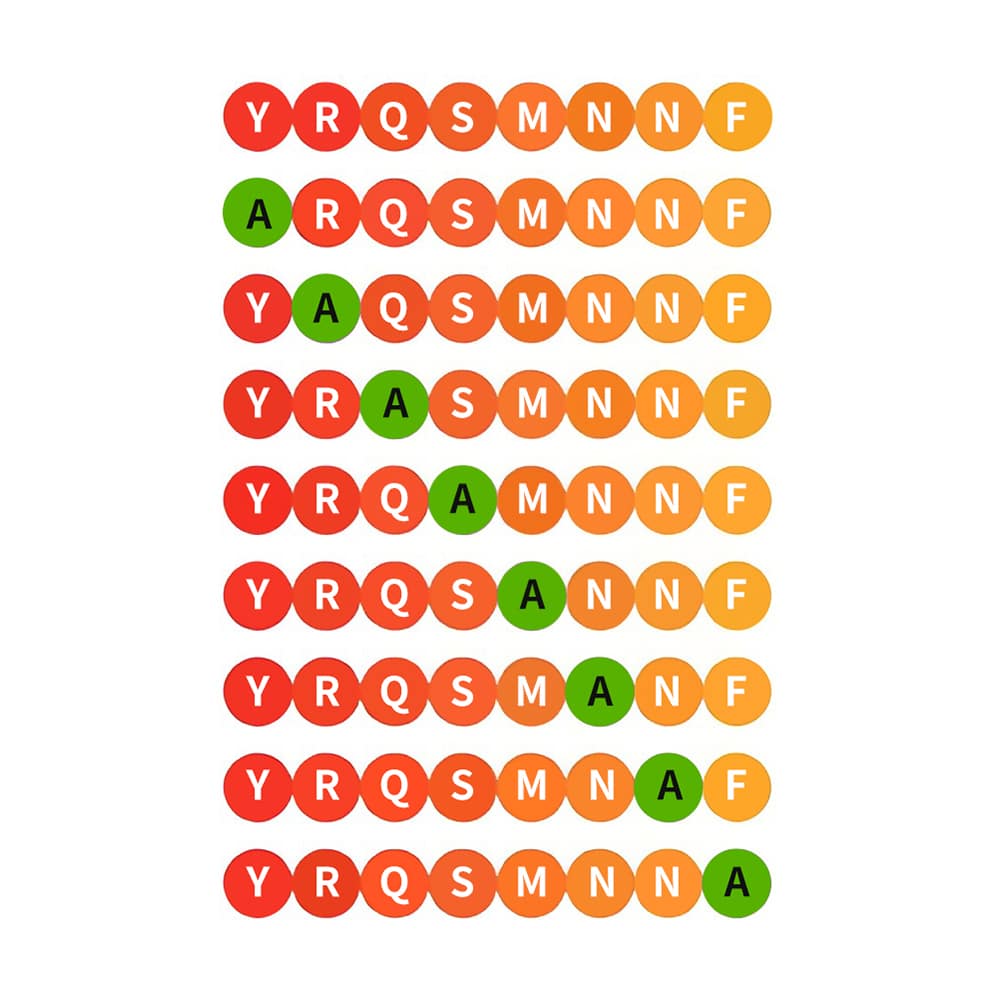
Alanine scanning libraries are applied to identify the specific amino acid residues, which determine the peptides’ function, stability, and conformation. Alanine is the smallest chiral amino acid. It is substituted sequentially for each non-alanine residue one at a time, then measure the corresponding change in epitope activity subsequently. The alanine substitution of key amino acid residues give rive to alternation in epitope binding activity. This library can determine the contribution of individual amino acid quickly in peptide’s functionality.
Positional scanning library
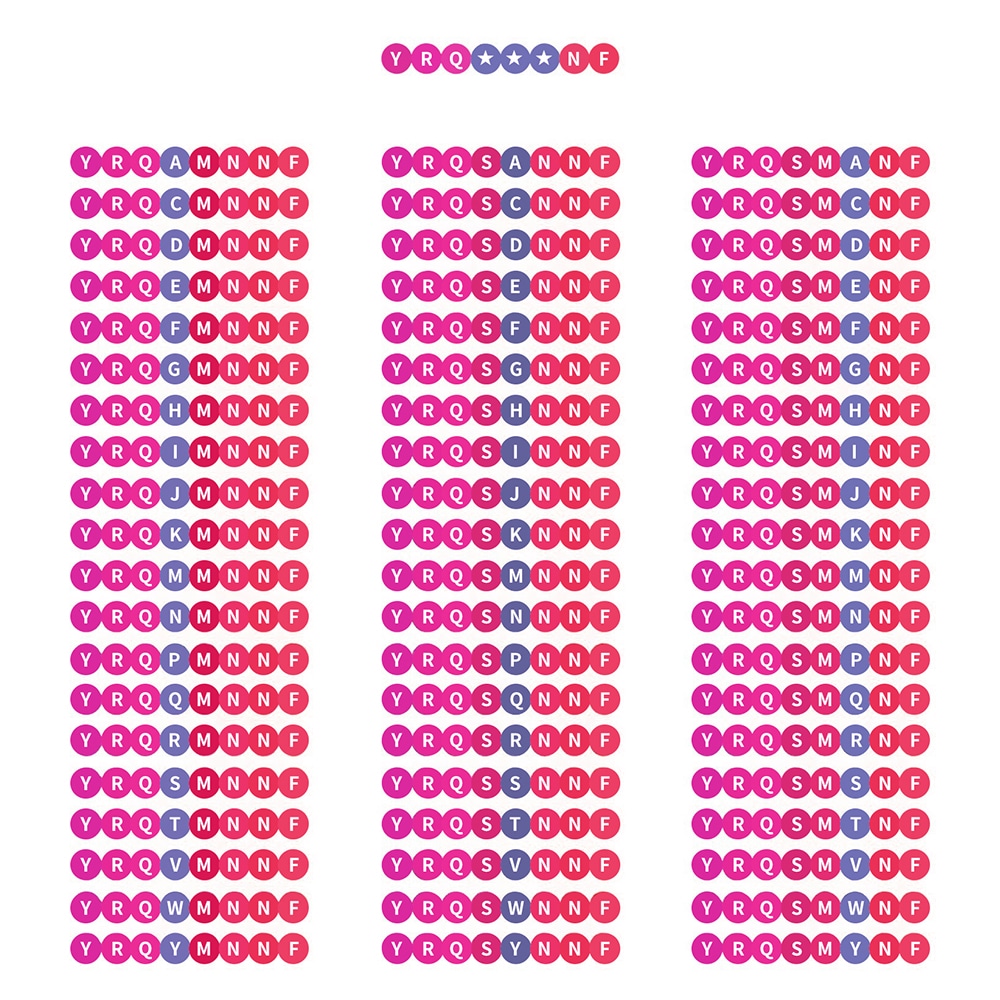
Positional scanning library is a critical tool for peptide sequence optimization. According to substitution of other natural amino acids at the given positions, it has the capability to identify amino acids for enhanced peptide activity. Particularly, positional scanning libraries are used to identify T-cell epitopes from complex mixtures of proteins. Besides, this type library also can locate substrates with interdependent subsites in minimum synthesis and screening.
Scrambled peptide library
The scrambled peptide library is constructed by conducting permutation on the original peptide’s sequence. It provides all possible alternatives and the highest variability degree for peptide library. The scrambled library has the highest variation of any peptide library. It can be applied to probe target molecules, such as proteins, antibodies, and DNA.
The practicality of peptide libraries synthesis is limited by peptide chain length, which has maximum of 70 amino acids. This restricts the study and research of larger proteins. Furthermore, the scope of peptide library should be narrowed down by specific selection of amino acids at desired point in the chain.
Large random peptide libraries are normally applied for certain peptide molecules synthesis, such as ultra-large chemical libraries for the discovery of high-affinity peptide binders. In addition, the increase in library size affects the parameters severely, such as synthesis scales, number of library members, sequence de-convolution, peptide structure elucidation. Therefore, the algorithm-supported design approach in peptide libraries is critical to address these technical challenges. This method can simplify the laborious permutation identification in complex mixtures, with base on molecular mass and amino acid diversity.
Peptide Library Design Guide
Peptide libraries become an invaluable tool for various research applications, like protein binding studies, cancer immuno-therapy, proteomics. It is cheaper and easier to identify critical & bioactive peptides by screening hundreds of peptides combinations simultaneously. However, selection of right peptide library can result in huge difference in research results. It is critical to consider the design guide, and ensure the best option for your research application.
Proteomics
| Design recommendations | |
| Service | Micro-scale peptide library |
| Design | Overlapping library design |
| Purity | Crude |
| Design details | 10 AA peptides, 2-4 AA overlap |
Peptide libraries are applied for various protemoic applications. Such as proteolytic peptide screening, or immune monitoring. Combining with mass spectrometry (MS), these peptide libraries can study reaction process, screen important biomarkers, identify post-translational modifications.
Cancer Research
| Design recommendations | |
| Service | Standard peptide library |
| Design | Overlapping library design |
| Purity | Crude or >70% |
Targeting therapeutics are critical for effective elimination of cancer cells, while peptide libraries are commonly applied for quick identification of important biomarkers on cancer cells. TAA (tumor associated antigens) related peptides are displayed screened in the library format. Once identified, specific antibodies are design for cancer immuntherapy or vaccines.
Vaccine Development
| Design recommendations | |
| Service | Standard peptide library |
| Design | Overlapping library or Alanine scanning library |
| Purity | High purity >90% |
As peptide libraries can span the entire protein sequence without miss of important epitopes, these libraries are applied commonly to identify immunogenic epitopes and evaluate vaccine effectiveness. In addition, vaccines should be tested first, but not recommended for certain infectious diseases. Therefore, peptide libraries are ideal for immune monitoring in vitro.
T cell immunotherapy
| Design recommendations | |
| Service | Micro-scale peptide library or Standard peptide library |
| Design | Overlapping library design and Truncated library design |
| Purity | Crude or >70% |
| Design details | Overlapping library: 10-15 AA peptides, 2-4 AA overlap |
| Truncated library: 8-12 AA peptides | |
Engineering T cells to target for elimination of viruses and cancer cells are the critical research areas. Immunotherapy is more efficient and effective, once engineering the receptor with specific TAAs or viral epitopes. Therefore, peptide libraries are invaluable to identify the antigenic sequences in design of T cell receptors.
Antibody and T cell epitope mapping
| Design recommendations | |
| Service | Standard peptide library |
| Design | Overlapping library, positional scanning library, or truncation library design |
| Purity | Crude or >70% |
The first step in immunotherapy development is identifying antigens for antibody stimulation and T cell binding. Once the positive T cell or antibody binding is confirmed, potential antigens are sequenced and separated into overlapping peptides. Then these peptide sequences are used to design targeted therapeutics.
Biological assays
| Design recommendations | |
| Service | Micro-scale peptide library or Standard peptide library |
| Design | Overlapping library or scrambled peptide library design |
| Purity | >70% or higher |
Individually aliquoted peptide sequences with large protein incorporation is ideal for various biological assays. These libraries are applied to identify peptides with antimicrobial activity, direct stem cell differentiation, or even pharmacological activity monitoring.
The practicality of peptide libraries synthesis is limited by peptide chain length, which has maximum of 70 amino acids. This restricts the study and research of larger proteins. Furthermore, the scope of peptide library should be narrowed down by specific selection of amino acids at desired point in the chain.
Large random peptide libraries are normally applied for certain peptide molecules synthesis, such as ultra-large chemical libraries for the discovery of high-affinity peptide binders. In addition, the increase in library size affects the parameters severely, such as synthesis scales, number of library members, sequence de-convolution, peptide structure elucidation. Therefore, the algorithm-supported design approach in peptide libraries is critical to address these technical challenges. This method can simplify the laborious permutation identification in complex mixtures, with base on molecular mass and amino acid diversity.
Custom Peptide Libraries
Custom peptide libraries are a rapid solution for a wide range of screenings, including peptides identification, antibody quantification, epitope mapping. QYAOBIO is able to manufacture customized peptide libraries with different size, peptide length and purity, peptide format.
Call Us
+86(021)-50795728
+86(027)-60707970
