Peptide Pegylation
PEGylation finally improve the pharmacokinetics of peptides.
QYAOBIO provides custom PEGlytaed peptide service in worldwide. Peptide PEGylation is the process of covalent linking one or more polyethylene glycol (PEG) chains to peptide molecules. PEGylation increases the peptides molecular mass, shield peptides from proteolytic enzymes, and finally improve the pharmacokinetics of peptides.
Peptides have the critical role in pharmaceutical industry and drug therapeutic development. However, peptide applications in vivo are limited by fast protease degradation, poor solubility, antigenic responses, and glomerular filtration in kidney. The covalent attachment of polyethylene glycol (PEG) can reduce immuno-genicity, improve solubility and reduce renal clearance. The addition of mono-dispersed PEG chains is the key factor in the PEGylated peptide therapeutic development. These safe and effective PEGylated peptides are critical for optimal therapeutic results.
Peptide PEGylation Service
PEGylation is the process of attaching PEG polymers to molecules, like peptides, proteins, and antibodies. In order to improve the safety and efficiency of therapeutics. This technology can alternate the physicochemical properties in conformation, electrostatic binding, hydrophobicity. Therefore, all these physical and chemical changes can increase systemic retention of the therapeutic agents, influence the binding affinity between therapeutic moiety and cell receptors, and alter the absorption and distribution patterns.
PEGylation is a well-established technology in targeting drug delivery systems. As more PEGylated therapeutics are approved by FDA, site-specific PEGylation attracts more attention, no matter discrete PEG or mono-dispersed PEG chains.
Site-specific PEGylation
Qyaobio can perform site-specific PEGylation at different sites on the peptides.
- N-terminal PEGylation is accomplished by direct PEG carboxylic acid coupling, or chemical ligation with PEG thioester and a cysteine residue.
- C-terminal PEGylation is a more complicated process. It is able to achieved by the thiocarboxylic acid modification and sulfone-azide PEG reagent. In addition, Hydrazide combine with a pyruvoyl reagent is another C-terminal PEGylation approach.
- Except N- and C- terminal, PEGlyation is nearly possible at any amino acid chains with the appropriate functional group.
PEGylation Methods
For PEGylated peptides, the PEGs are normally attached to peptides by standard amide bond formation. However, in order to ensure the site-specific PEGylation, there are 3 common comethodologies:
- Click Chemisty: This reaction takes place between the azide group of PEG reagents and the alkyne group of peptides, or vice versa.
- Suzuki-Miyaura Coupling: It takes place between the iodophenyl group of PEG reagents and the aryl boronic acid group of peptides, or vice versa.
- Sonogashira Coupling: This takes place between the iodophenyl group of PEG reagents and the alkyne group of peptides, or vice versa.
PEGylation Advantages
PEGylation impart several pharmacological advantages over the unmodified forms by the increase of molecular weight. Such as increased drug solubility, improved drug stability, reduced dosage frequency without diminished efficacy, reduced potential toxicity, extended drug circulating life, enhanced protection from proteolytic degradation.
PEG Derivatives for Peptide Synthesis
PEG derivatives (PEGs) are applied in custom peptide synthesis to improve solubility of hydrophobic peptides, enhance bio-availability of bio-active peptides, and protect peptides from triggering immune responses. As polyethylene glycol (PEG) derivatives are amphiphilic, PEGylation can improve the solubility of peptides in both aqueous and organic solvents. Bifunctional PEGs (PEG amino acids) are common linkers and spacers for peptide conjugating, fluorescent labels. These PEG derivative can be applied in both SPPS and LPPS.
PEGs are nonionic, nontoxic, biocompatible, and highly hydrophilic polymers. PEGylated peptides can overcome many challenges for peptide drug candidates. PEGylation is a popular method to improve peptide stability and bio-availability.
Monodispersed PEG
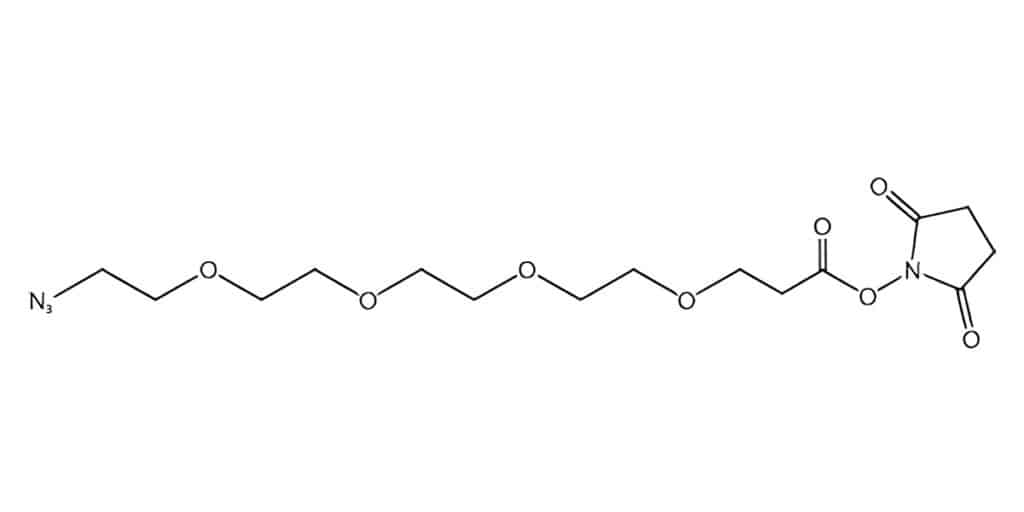
Monodispersed PEG is composing of precisely-defined number of PEG units. As the shorter PEG length, it is available to define length of polyethylene glycol derivatives. These short PEGs are applied as linkers or spacer in peptide conjugations. Such as PEG spacers are versatile tools to attach sensitive molecules (fluorophores) to peptides, or to create homo-dimeric, hetero-dimeric peptides.
Polydispersed PEG
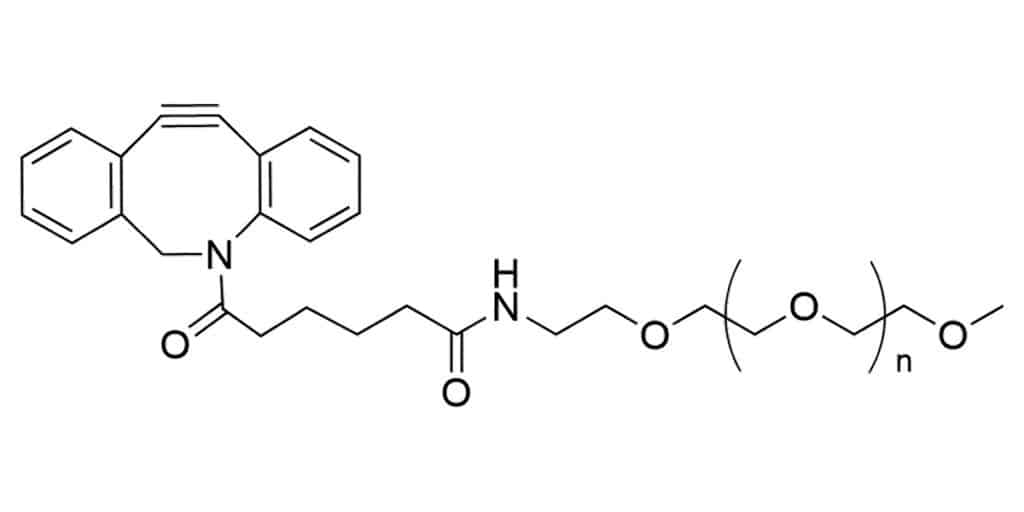
PEGs with more than 60 atoms in length are generally consisted of different olilgomer sizes in broad molecular weight ranges. As these PEGs are difficult to defined precisely, they are referred to as polydispersed PEG. Such as PEG1000 denotes a mixture of PEG molecules with average of 10000 molecular weight (n=195 to 265).
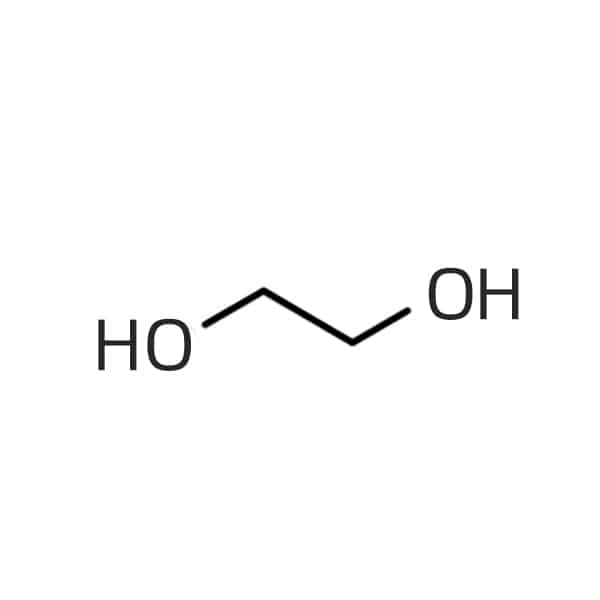
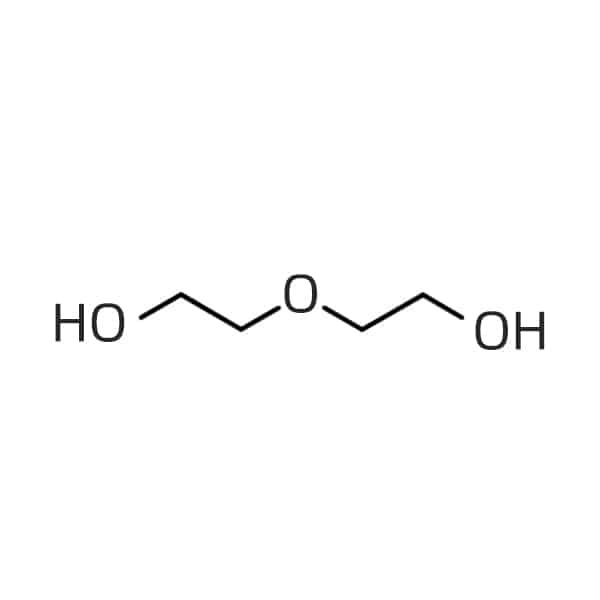
Common PEG Abbreviations
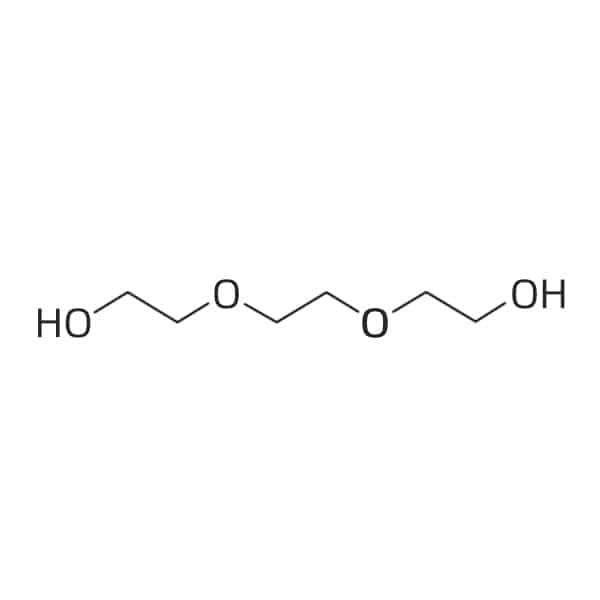
PEG
PEG2
PEG3
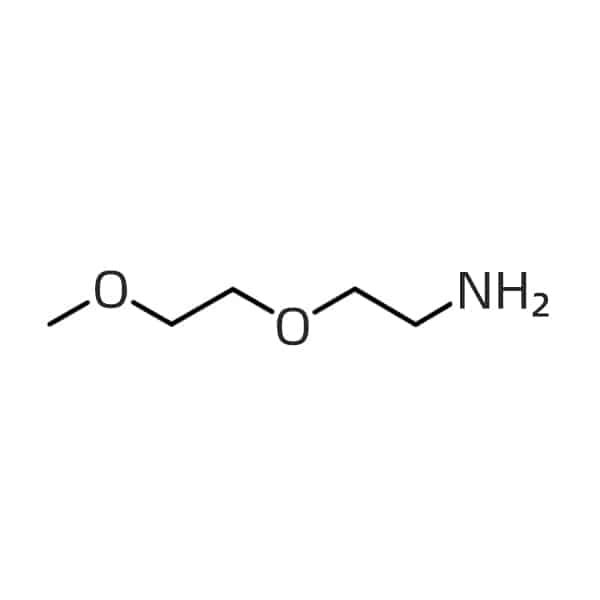
m-PEG2-amine
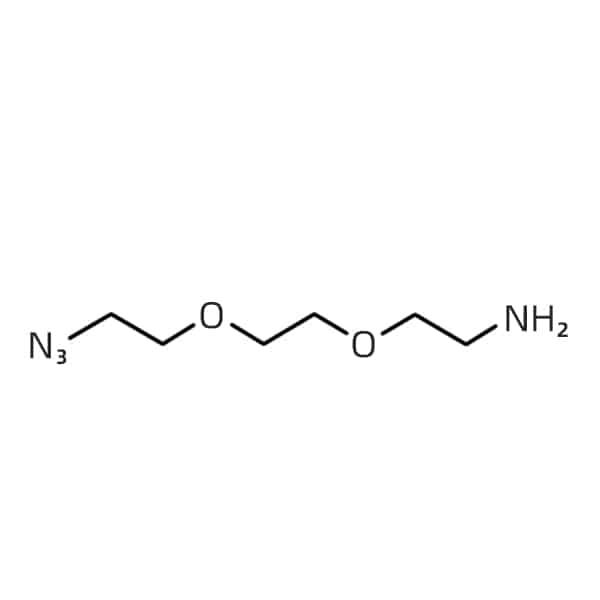
azido-PEG2-amine
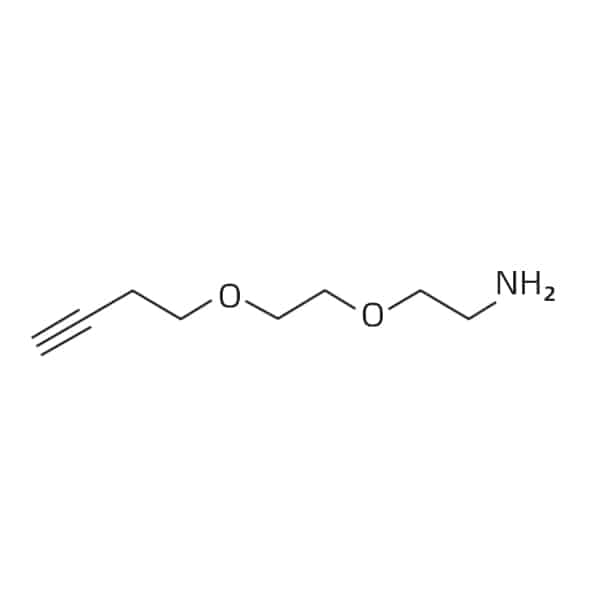
propargyl-PEG2-amine
amino-PEG2-amine
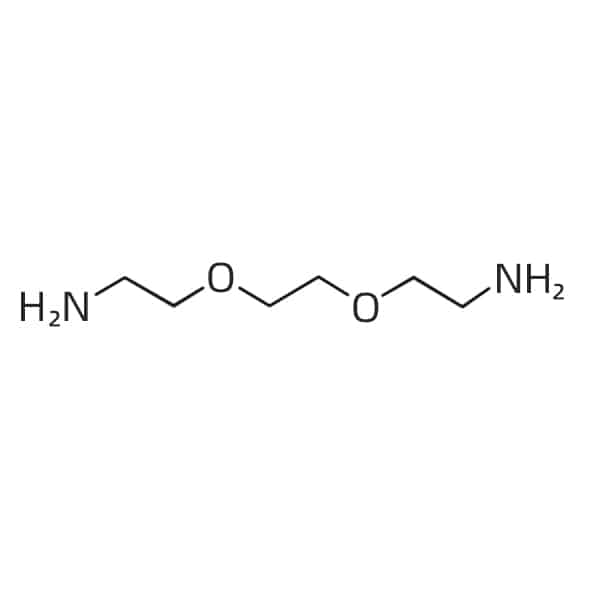
amino-PEG2-acid
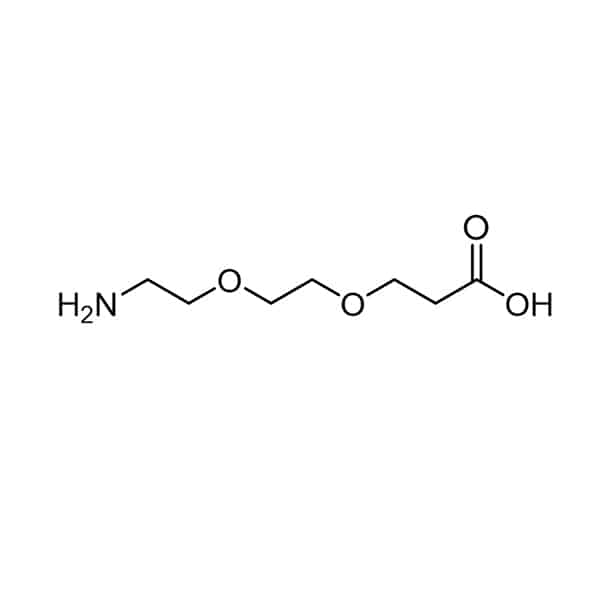
Custom PEGs
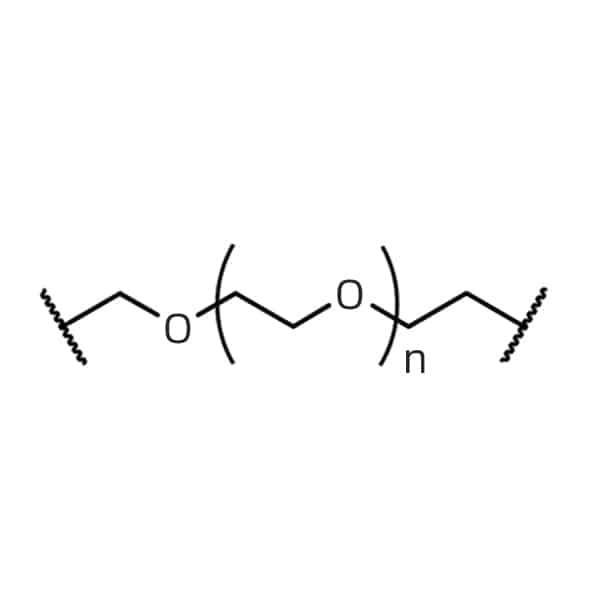
biotin-PEG2-amine
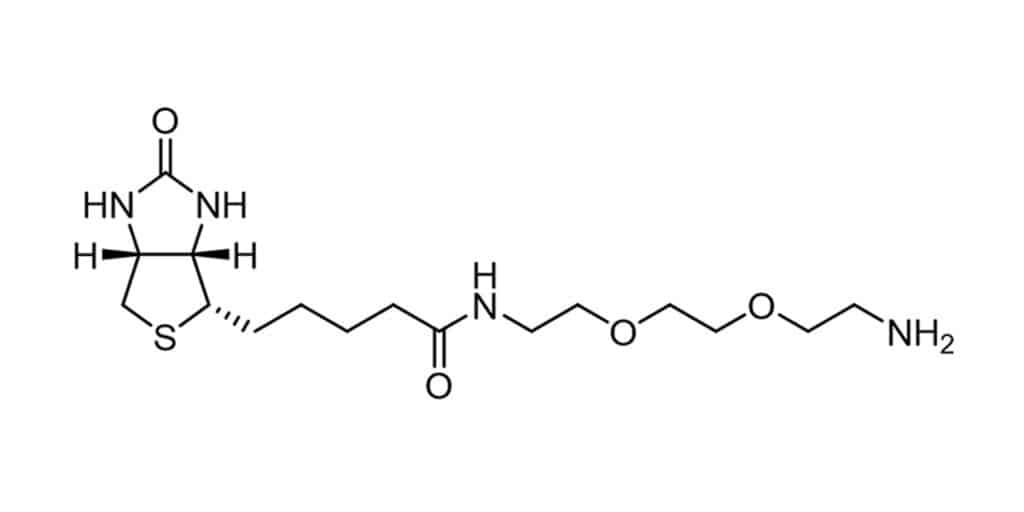
mini-PEG3
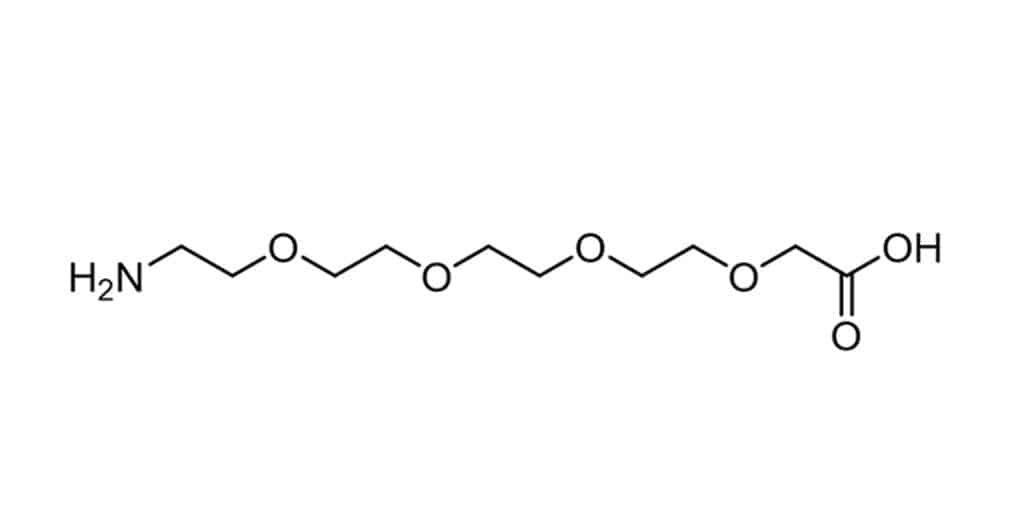
PEG8
Peglation Improvement
PEGylated Peptides Performance
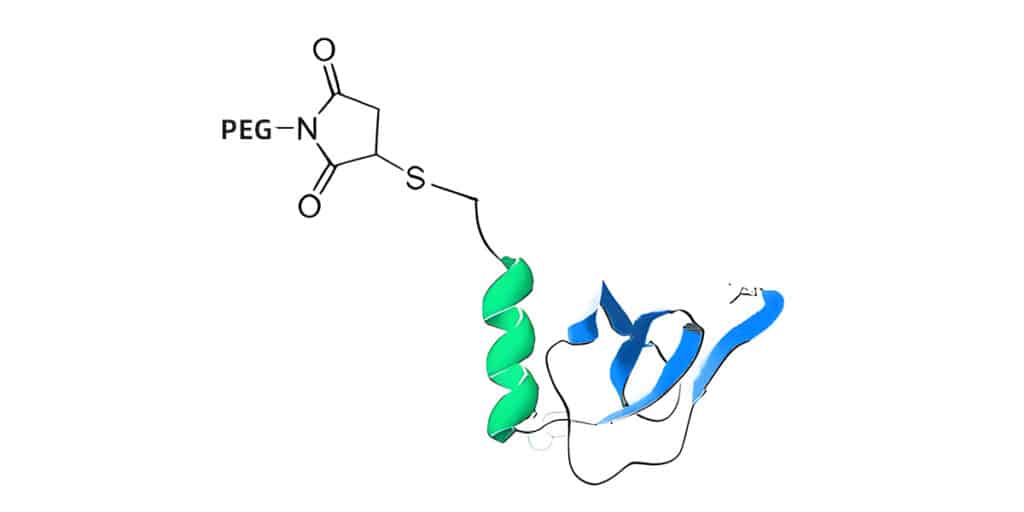
There are four factors affect the performance of PEGylated peptides:
- Molecular weight and structure: PEGs with MS under 1000 Da can be broken down into sub-units with toxicity, while PEGs over 1000 Da have non toxicity in vivo.
- Number of PEG chains: the total molecular weight of PEGs can increase by addition of more lower-weight chains.
- Specific-site attachments: the specific-site of PEGylation are engineered carefully in experiments, in order to retain the highest binding efficiency and activity of peptide ligands.
- PEGylation chemistry: the linkage type between PEG and peptides, the purity of raw materials, intermediates and final products. The purity is the most critical factor to determine the yield and scalability of PEGlation manufacturing. Peptides and PEGs must be pure and stable during conjugation reaction for efficient conjugates.
Qyaobio provides cost-effective PEGylation for peptide modification, in order to improve the bioavailability of molecules.
Peptide Bioavailability in PEGylation
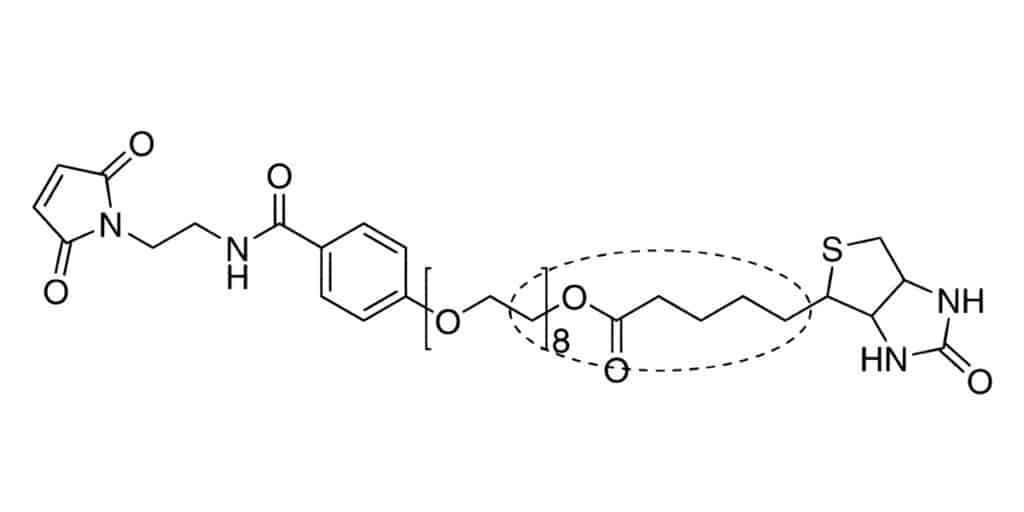
PEGylation provides multiple physicochemical and pharmacokinetic benefits for therapeutic peptides. The PEG-peptide conjugates have longer blood circulation time, increased solubility, and reduced immunogenicity.
Longer circulation time with enhanced bioavailability results in lower dosing frequency and amount. In addition, the increased steric hindrance of PEG chains can hinder the interactions of non-specific protease. N-terminal PEGylation can block endopeptidases specially, and provide steric hindrance to proteolyic enzymes. Furthermore, PEG chains can also block the peptide epitopesite from antibody binding.
PEG Spacer/Linker
As the advancement of more sensitive and non-invasive imaging techniques of PET (Positron Emission Computed Tomography), SEPCT(Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography), Spacers/linkers between the peptide and chelate (DOTA, NOTA) are incorporated to improve the binding affinity. PEG spacers provide advantages over hydrocarbon spacers because of the higher hydrophilicity. There is profound increase in tumor uptake and retention with PEGylated RGD-based probes observation. The PEG linkers with inert and flexible characteristics provide distance between the cargo carrier (NOTA) and receptor for optimal binding
Qyaobio Advantage in PEGylation
- Cost-effective synthesis in custom peptides
- High skilled and scientific staff
- Specialize in synthesis of monodispersed PEG derivatives
- Superior technical support
- Quality assurance of HPLC and MS analysis
Call Us
+86(021)-50795728
+86(027)-60707970
