Affinity Chromatography Purification
QYAOBIO provides affinity chromatography protein purification for customers in worldwide
Affinity chromatography (AC) utilize the reversible interaction between target proteins and specific ligands on the chromatography base matrix, in order to separate the target proteins. This interaction is bio-specific, such as: antibodies binding to protein A, the receptor binding to hormones. Or non-biospecific, such as: proteins binding to the dye substance, histidine-proteins binding to metal ions (immobilized metal ion affinity chromatography- IMAC).
Common Affinity Tags
Affinity tags are the short peptides added to either N or C terminals of recombinant proteins, in order to facilitate purification of the expressed proteins. The affinity tags normally contain amino acids from several to hundreds. In QYAOBIO, we provide the most common affinity tags by affinity chromatography:
His Tagged Protein Purification
His-tagged protein purification requires the His-tag and Ni-NTA interaction. This is based on the selectivity and high affinity of Ni-NTA(nickel nitriloacetic acid) reins for proteins containing his tag.
GST Tagged Protein Purification
In GST fusion purification, GST tagged proteins bind to immobilized glutathione (GSH Bind). Then nonbinding proteins are washed away from the matrix (Wash). Finally, elute the bound GST fusion proteins from the support (Elute).
FLAG Tag Protein Purification
FLAG-tagged proteins can be purified directly from the cell culture lysate or supernatant. The FLAG-tagged proteins can bind to the specific monoclonal antibodies conjugated on the agarose gel. After washing away residual impurities, the bound FLAG-tag proteins are eluted off the affinity column by high concentration FLAG-tag peptide or low pH buffer.
SUMO Tag Purification
SUMO proteins are similar to ubiquitin in folding structure, but only about 20% homology to the amino acid sequence. SUMO proteins can conjugate to substrate proteins in similar to ubiquitin. Then, SUMO attachments are removed by SUMO-specific isopeptidases just like UCHs and UBPs remove ubiquitin from substrate proteins.
Specific Application
In affinity chromatography process:
- The target proteins are reversibly and specifically bound to the complementary binding substance(ligand). The samples are applied under conditions with favorable binding, then unbound materials are washed out from the column.
- The target proteins recovered by changing conditions for favoring elution. The elution can be performed specifically, like the competitive ligand. Or non-specifically, like change of pH, ionic strength, polarity. Finally, the target proteins are eluted in purified and concentrated form.
Since the high selectivity, affinity chromatography is applied for single-step purification. More commonly, AC is used as the first capture step, the followed by one or more steps to remove remaining impurities. Such as: protein A or protein G ligands with agarose base matrix are suitable for routine purification of antibodies.
Normally, most laboratory-scale purifications are performed with affinity-tagged proteins. For example, Histidine-tagged proteins are purified by IMAC, Glutathione S-tranferase (GST)-tagged proteins are purified by chromatography resin with immobilized glutathione. In addition, affinity chromatography is also utilized to remove specific impurities.
Affinity Tag Application
Affinity chromatography are implied for purification of the target proteins via affinity tags, there are some application in addition to the normal purification, including:
Detection
Since specific antibodies are available for most affinity tags, the tagged proteins can be detected via immuno-staining, in Western Blots, ELISA Assays.
Immobilization
Affinity tags can immobilize tagged proteins on surface of plasmon resonance chips, ELISA plates.
Pulldown
Affinity-tagged proteins are pulled down from complex solutions by magnetic beads. They are also utilized to pull-down interaction partners from complex mixture by affinity beads.
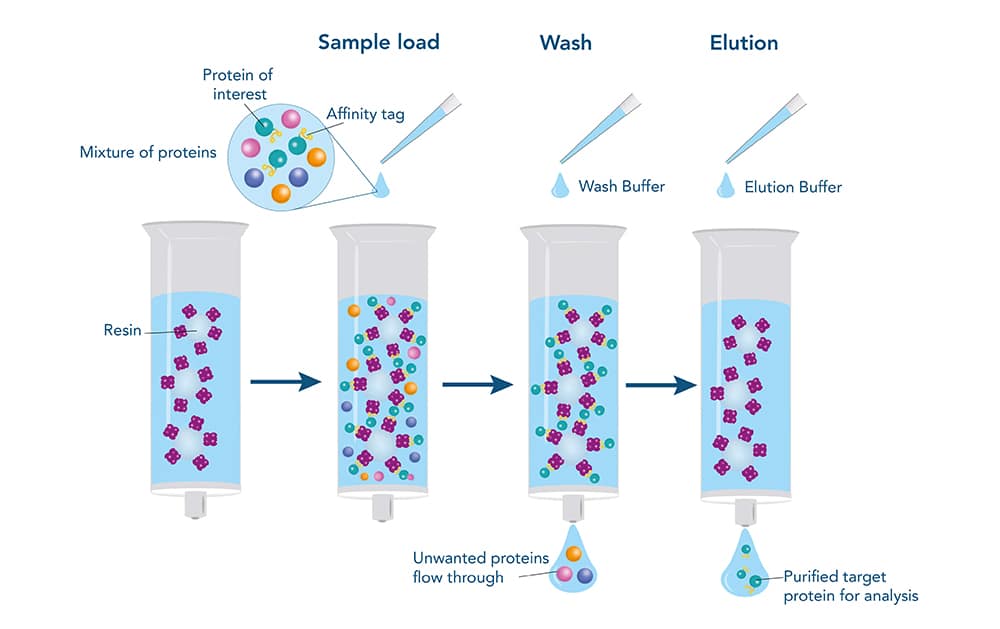
AC Purification Steps
In affinity chromatography, target proteins are loaded on the column by binding between the proteins and ligands. Then contaminating proteins are washed away. Finally, the bound proteins are eluted by different buffers, containing with either competitive molecules or condition disrupt all interactions. These competing molecules are removed typically removed through either chromatographic procedure or dialysis. Most affinity purification involves the following steps:
Binding
The complex solution with the tagged proteins are incubated to the column with the affinity support. In order to ensure the binding based on the affinity tag – matrix interaction.
Washing
Wash away the non-bound sample components from the support by appropriate buffers. These buffers can maintain the binding interaction between target proteins and ligands, while other proteins without specific bind are washed away.
Elution
Elute the target proteins from the immobilized ligands by altering the buffer conditions. Specific bonding proteins are eluted by competitive binding of similar molecules, like histidine and imidazole. Otherwise, cutting off the tags with proteases, or destabilize the interaction between the affinity tag-matrix (change of pH).
Affinity Chromatography Ligand and Conditions
| Protein to Purify | Ligand | Eluting Condition |
| Polyhistidine-tagged protein | Ni2+ or Co2+ | Imidazole or free histidine |
| FLAG-tagged protein | FLAG-specific antibody | FLAG peptide or low pH |
| GST-tagged protein | Reduced glutathione | Free glutathione |
| Myc-tagged protein | Myc-specific antibody | Low pH |
| Antibody (antigen-specific) | Antigenic peptide | Free peptide |
| Antibody (class-specific) | Protein A , G, or L | Extremes in pH |
| DNA-binding protein | Heparin | High ionic strength |
Ni-NTA Chromatography Purification
Ni-NTA Agarose is an affinity chromatography matrix for recombinant proteins purification with the His tag. Hisidine residues in the His-tag can bind to the vacant position in the coordination sphere of the immobilized nickel.
The cleared cell lysates are loaded to the matrices, only his-tagged proteins are bound, other proteins pass through. After washing, the his-tagged proteins can be eluted in buffer under native or denaturing conditions.
Binding & Elution Buffers
Binding buffers are applied in most affinity purification procedures with protein-ligand interactions. Especially in for affinity purification with interaction basis of antibody-antigen or native protein-protein.
Once the binding interaction finish, the additional buffers are utilized to wash support and remove non-bound components in the samples. Finally, elution buffers are added to disrupt the binding interaction, and release the target molecule, then collected in purified form. Elurion buffers normally dissociate the binding partners by extreme of pH (low or high), high salt (ionic strength). In most cases, subsequent dialysis or desalting are required to exchange the purified proteins from elution buffers for storage or downstream analysis.
Solid Supports for AC Purification
Affinity purification separates the molecules on the base of binding interaction with ligand on the solid support. The support or matrix are normal materials with covalently attachment with bio-specific ligands. There are hundreds of substances in affinity matrices, including agarose, dextran, cellulose, polyacrylamide, latex, controlled glass.
The useful affinity supports have common characteristics: high surface-area to volume ratio, chemical groups with easily covalent to ligands, minimal nonspecific binding properties, good flow characteristic, mechanical and chemical stability.
Call Us
+86(021)-50795728
+86(027)-60707970
