Mixed Mode Chromatography
QYAOBIO provides mixed mode chromatography purification for customers in worldwide
Mixed-Mode Chromatography (Multimodal Chromatography) is the chromatographic methods to utilize more than one form of interactions between the stationary phase and analytes. Distinct from conventional single-mode chromatography, the secondary interactions in mixed-mode chromatography should not be too weak, this contributes to the retention of the solutes.
MMC Advantages
Mixed-mode chromatography is advantageous for intermediate purification, it is the new option in challenging purification workflow, such as high conductivity binding and alternative selectivity. MMC are alternative solution for effective protein purification, such as:
- Insufficient selectivity of resins for the required purity
- Salt tolerance, once the loading conductivity of samples is too high for traditional resin
- Require to reduce purification steps
Higher Selectivity
Positive, negative, neutral substances can be separated by the reversed phase(RP)/anion-cation exchange(ACE) column in one single run.
Higher Loading Capacity
Comparing to the RPLC (Reversed phase liquid chromatography), the loading capacity of ACE/hydrophilic interaction chromatography(HILIC) increase about 10-100 times.
Higher Efficiency
One mixed-mode column can replace two or more single-mode columns, this can ensure the high efficiency.
MMC Classifications
Mixed-Mode Chromatography are normally classified into physical MMC and chemical MMC. In physical MMC, the stationary phase is constructed of two or more kinds of packing materials. In chemical MMC, apply just one packing material with two or more functionalities.
Physical MMC
- The simplest method is tandem column, connect two commercial column in series.
- Another is bi-phasic column, pack two stationary phases separately in the same column.
- The third approach is hybrid column, or mixed-bed column, homogenize two or more types of stationary phases in one single column.
Chemical MMC
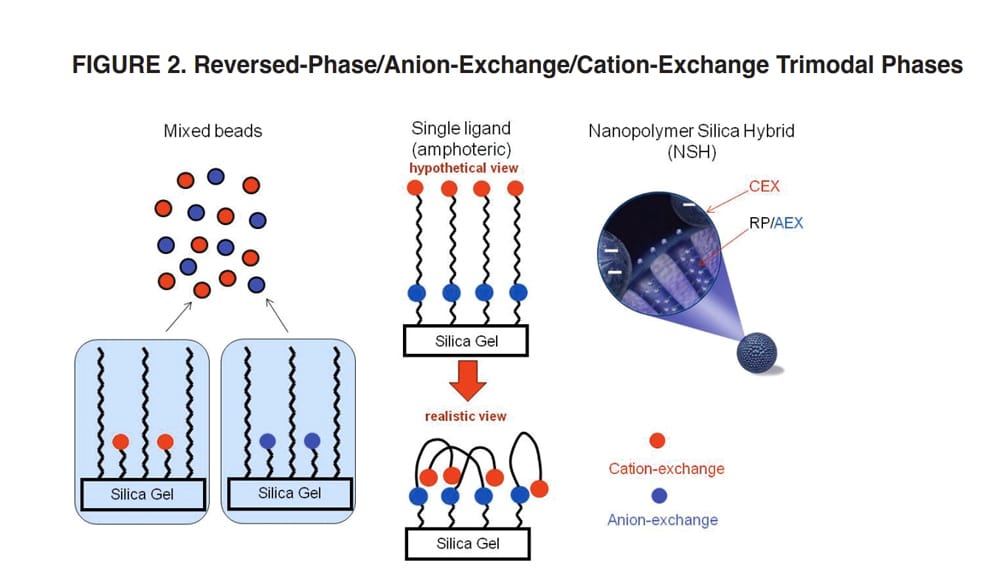
IEC/HIC
Ion exchange chromatography/Hydrophobic interaction chromatography have the closest conditions for biological activity maintenance. This combination is applied widely for biological separations. IEC/HIC can apply both electrostatic and hydrophobic interactions, this can improve separation powder and selectivity.
IEC/RPLC
Ion exchange chromatography/Reversed Phase Liquid Chromatography combine the advantage of RPLC and IEC. Comparing to single RPLC, this IEC/RPLC technology increase separation powder and freedom degree of selectivity.
HILIC/RPLC
Hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography/Reversed Phase Liquid Chromatography show RPLC or HILIC retention by adjustment in mobile phase.
HILIC/IEC
Hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography/Ion exchange chromatography provide unique selectivity, stronger separation powder, wider application range in protein separations.
SEC/IEC
Size exclusion chromatography/Ion exchange chromatography allow us to apple SEC column as the weak ion exchanger, due to the electrostatic effect contribution to retention significantly in protein SEC.
Mixed-Mode Chromatography Process
The common process in Mixed-mode chromatography are four steps:
Equilibration
Prepare the column to starting conditions, once reach equilibration, all charged groups are associated with exchangeable counter ions as chloride or sodium ions.
Sample Application and Wash
Target proteins bind to ligands via multi-modal interactions, the sample buffers have the same pH and ionic strength as the starting buffer.
Elution
Change the buffer composition and pH, in order to release target proteins from the stationary phase.
Regeneration
Remove all molecules still binding to the stationary phase, ensure the full capacity of available resins.
Call Us
+86(021)-50795728
+86(027)-60707970
