Size Exclusion Chromatography
QYAOBIO provides size exclusion chromatography for customers in worldwide
Size exclusion chromatography (SEC), is also known as gel filtration chromatography. It can separate molecule with different size through the gel filtration. The gel consists of spherical beads with pores of specific size distribution. The separation occurs once different molecules are included or excluded from the pores in the matrix.
The small molecules diffuse into the pores, their flow through the column is retarded according to molecule size. While large molecules never enter the pores, and only elute in the column void volume. Therefore, molecules are separated by size, and eluted in order of decreasing molecular weight (MW).
Operation conditions and gel selection are determined by the application and desired resolution. Two common types of separations by SECF are fractionation and desalting (buffer exchange)
- Fractionation: molecules with different MW are separated within the gel matrix.
- Desalting: common use of SEC for desalting proteins or nucleic acids.
Mechanism of Size Exclusion
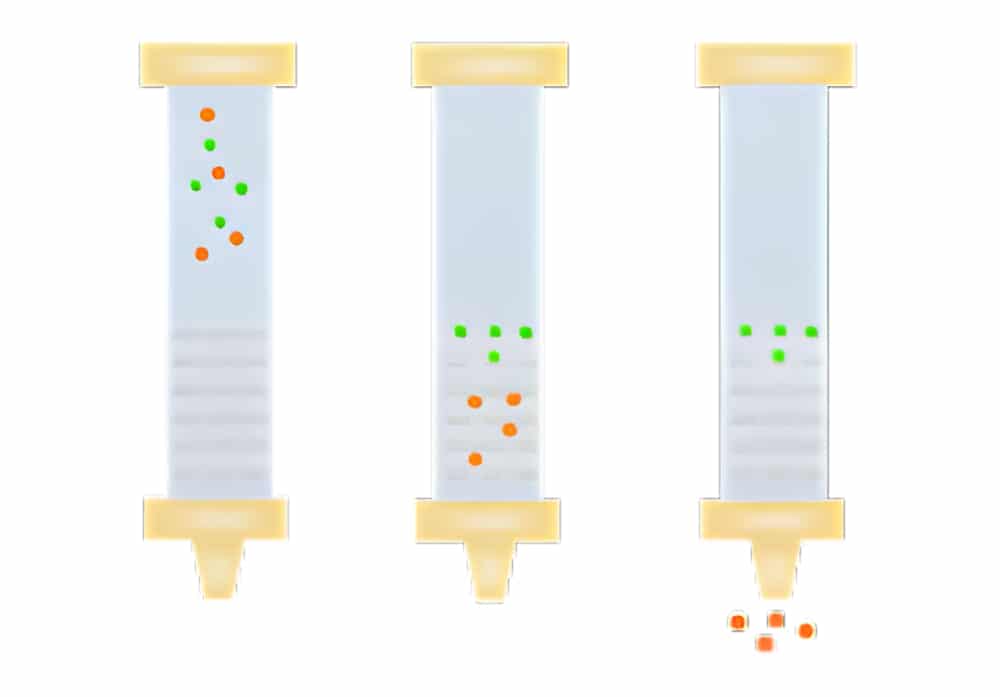
SEC (Size exclusion chromatography) resins consist of spherical particle with porous matrix, these beads are lack reactivity and adsorptive properties. Once the samples enter into the column, molecules larger than the pores cannot diffuse into the beads, so these molecules elute firstly. If the molecules’ size is smaller than the smallest pores in the resin, they are able to enter the total pore volume, these size molecules are eluted lastly. Other molecules between these two sizes can penetrate the pores in varying degrees. Since the samples are eluted isocratically, there is no need of different buffers in the separation process.
SEC resins for bio-molecules purification have the designed fractionation range, this defines the molecular weights (MW) range access to the pores partially. Fractionation ranges of MW between 100 to 7000 are suitable for separation of peptides and other small molecules, while between 100,000 and 300,000 are excellent for larger protein or antibody purification. The exclusion limit of resins indicate the molecules’ size, which can be excluded from the pores and eluted in the void volume.
Particle size, column dimension, minimizing system volumes, flow rate, column packaging, all these factors are critical for high-resolution peak. The selectivity of resins together with efficiency will affect the resolution between peaks. The resin selection depends on the properties of resins, like pore size distribution, interaction between sample and resin, applied conditions. The resin efficiency depends on the particle size, column format, and column packing.
SEC are utilized in different roles, including desalting (buffer exchange), non-protein contaminants removal (DNA, viruses), removal of protein aggregate, biological interaction and protein folding research.
General Considerations in SEC
Fractionation
SEC cannot discern the similar MW species, but it is excellent to separate molecules, which is not fully resolved by IEX or HIC. Therefore, it is usually reserved as the final step of purification. The resolution of separation depends on particle size, pore size, flow rate, column length and diameter, sample volume.
Analysis
SEC can measure the molecular weights of unknown molecules with proper column calibration of MW standards. It is quire accurate for globular proteins in molecular weight estimation by column chromatography, but less accurate for linear molecules like DNA.
Desalting
In desalting, the MW difference between proteins and salt are so large, these peaks are less likely to overlap. Therefore, it is possible to apply shorter and wider columns.
Preparative SEC for Protein Purification
Preparative SEC is a high resolution size-based separation technology with collection fractionation for further analysis or scale-up. It can isolate one or more component from one sample.
Resins and Prepacked Columns
Preparative SEC is a high resolution size-based separation technology with collection fractionation for further analysis or scale-up. It can isolate one or more component from one sample.
Optimizing SEC Separation
The success of SEC separation depends primarily on the effect of sufficient selectivity and counteract peak broadening. The common optimization process:
- Select a resin with the suitable fractionation range for optimal resolution.
- Choose a column with the bed height for required resolution.
- Select the suitable column size for sample volume.
- Choose the highest flow rate to maintain resolution and minimize separation time.
Analytical SEC for Protein Purification

Analytical SEC is an effective method for protein analysis. Due to the mild separation conditions, it provides size profiling of protein samples. The common application are:
- Study complex formation
- Evaluate protein stability
- Evaluate protein aggregate and quantity
- Evaluate protein degradation and form quantity
- Identify protein interaction partners and conditions
Analytical SEC can be applied to check the quality and study the properties of proteins. Normally, the prepacked columns are excellent choice for reliable results and conveniences. Analytical SEC is also used for rapid purity checks and screening.
The most common resins in analytical SEC are either silica or agarose. The agarose is from natural sources with small amount of ionic and hydrophobic groups, which can interact with the compounds of proteins. In contrast, silica-based resins require coating of silanoal groups
Desalting and Buffer Exchange
Size exclusion chromatography (SEC) is applied widely in group separation, like desalting, buffer exchange. It can separate small molecules (salts) from large bio-molecules (protein). The main group separation including:
- Removal of free low-molecular labels
- Termination of reactions between macro-molecules
- Removal of un-reacted radio-labels
Desalting and buffer exchange can applied before, between, or after purification.
Call Us
+86(021)-50795728
+86(027)-60707970
