QYAOBIO Resource
Common FAQ, Blog, Publication, White paper in peptide synthesis
Common FAQ
Custom peptide synthesis FAQ
Common FAQ
Custom Antibody Production FAQ
Common FAQ
Custom Protein Production FAQ
Peptide information
Professional Peptide Blog
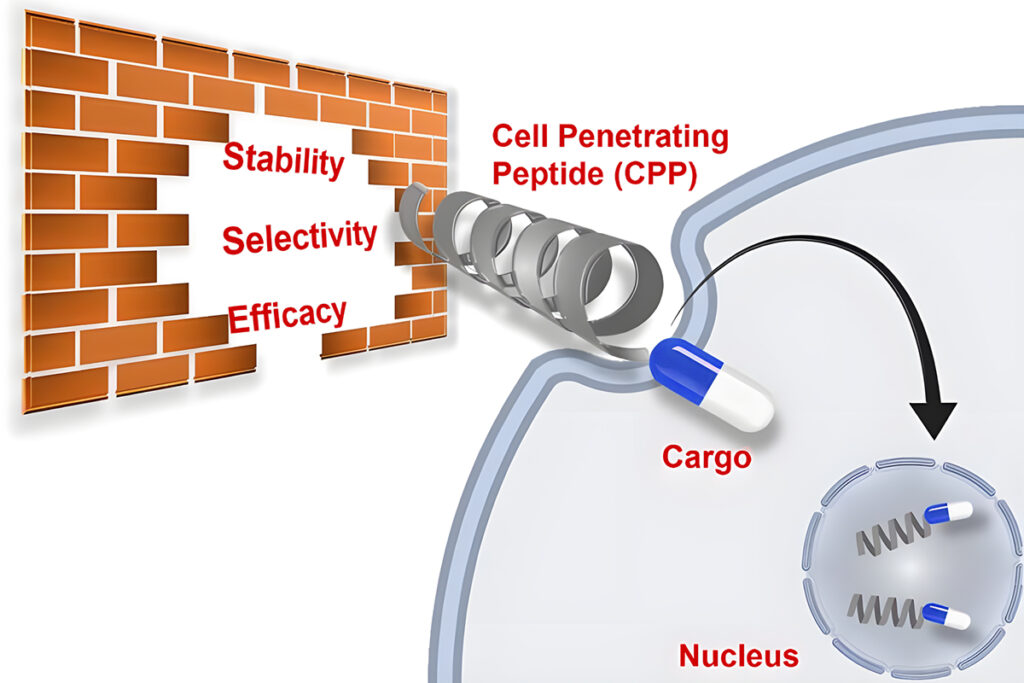
Design Strategy for Cell Penetrating Peptides
Cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs) have the ability to penetrate biological membranes and drive cells to internalize a bioactive payload.
Peptide Library Synthesis
There is a growing need for highly efficient synthetic peptide library systems, due to recent developments in the discovery of novel drug targets.
Synthesis of Multi Antigenic Peptides
Multiple antigen peptides (MAPs) are a kind of polymeric peptide macromolecules bearing radial branches.
Antigenic Peptides Design
Antigenic peptides are synthesized via short amino acid sequences derived from carefully selected native target proteins.
Chemical Synthesis of Unnatural Amino Acids
Unnatural amino acids (UAAs) not exist in natural polypeptide chains, so they are considered non-proteinogenic amino acids.
RGD Peptide
RGD peptide is a synthetic peptide with the sequence GRGDSPK, which binds to integrins (receptor family of extracellular matrix proteins).
Stapled Peptides for Drug Improvement
Stapled peptides are the new technology to bypass the intrinsic problem of peptide-drugs, this new strategy will increase the cellular uptake.
Optimize Peptoid Synthesis
QYAOBIO can synthesize polypeptoids with various modifications for selected synthetic targets.
Chemo Enzymatic Peptide Synthesis
Chemo enzymatic peptide synthesis (CEPS) is a cutting-edge technology with the unique versatile engineered enzymes.
Lipopeptides and Lipoglycopeptides
Lipopeptides and lipoglycopeptides are antibiotic classes with activity against gram-positive bacteria on the bacteria cell wall.
Amide Bond Formation in Cyclization
There are three main peptide coupling reagents for amide formation: carbodiimides, phosphonium, and aminium−/uronium–iminium reagents.
C-C Bond Cyclic Peptide Formation
The new carbon-carbon bond will form by reductive elimination. Most typical C-C cross couplings are used to synthesize peptide macrocycles.
Peptide Macrocyclization Strategies
Macro-cyclic peptides are a critical molecular format, these peptides combine advantages of small-molecule and biological therapeutics.
Fluorescent Peptides for Research
The advent platform of fluorescent peptides can enable advance research in cell system researches, fluorescence or FRET energy transfer.
AMPs Introduction
Antimicrobial peptides are class of small peptides with widely natural exist, AMPs are the important part of the innate immune system.
Click Chemistry in Peptide Synthesis
Click chemistry can generate substances by joining small azide and alkyne units together, and generate structural diversity in peptides.
Glycosylation of Peptides
Glycosylation of peptides is a promising synthesis strategy, it can modulate the physico-chemical properties of peptide drugs.
Call Us
+86(021)-50795728
+86(027)-60707970