RGD Peptide
Introduction
RGD peptide is a synthetic peptide with the sequence GRGDSPK, which binds to integrins (receptor family of extracellular matrix proteins), thereby playing an important role in cell adhesion, migration, growth and differentiation. The RGD-sequence was originally discovered as the minimal binding epitope of fibronectin for cell attachment and widely found in extracellular matrix proteins (ECM), including fibronectin, fibrinogen, vitronectin, osteopontin, etc. This sequence peptide is recognized by about half of the more than 20 known integrins in their adhesion protein ligands. RGD peptide inhibits integrin-ligand interactions and can induce apoptosis in the absence of signaling and integrin-mediated cell clustering.
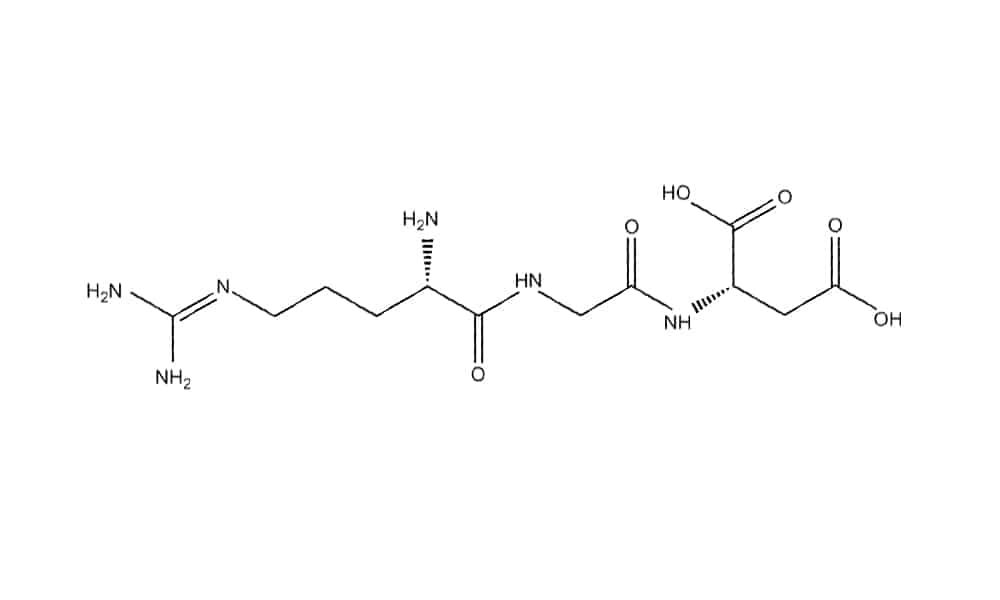
Linear RGD Integrin Inhibitory Peptides
It has been reported that RGD sequence activity is greatly affected by the presence and chemical nature of flanking residues. The following linear peptides are utilized in research: RGD, RGDS, GRGD, GRGDS, GRGDSP, and GRGDSPK. Initially they were used to bind to integrin subtypes αvβ3 and αvβ5, with relatively good IC50 values for binding to α5β1 and αvβ6, but with low affinity for αIIbβ3. In addition to the above-mentioned compounds, GRGDNP and GRGDTP peptides are also frequently used in biological research, and GRGDNP prefers to bind to α5β1. All linear peptides exhibit strong affinity for αvβ3, followed by αvβ5 and α5β1, and are selective for αvβ6, αvβ8 and αIIbβ3. The binding affinity of residues flanking the RGD motif essentially contributes to αvβ3, whereas there is a lesser extent to α5β1 and αvβ5. Specifically, the linear heptapeptide GRGDSP significantly enhanced the binding capacity to αvβ3 when compared to the tripeptide RGD.
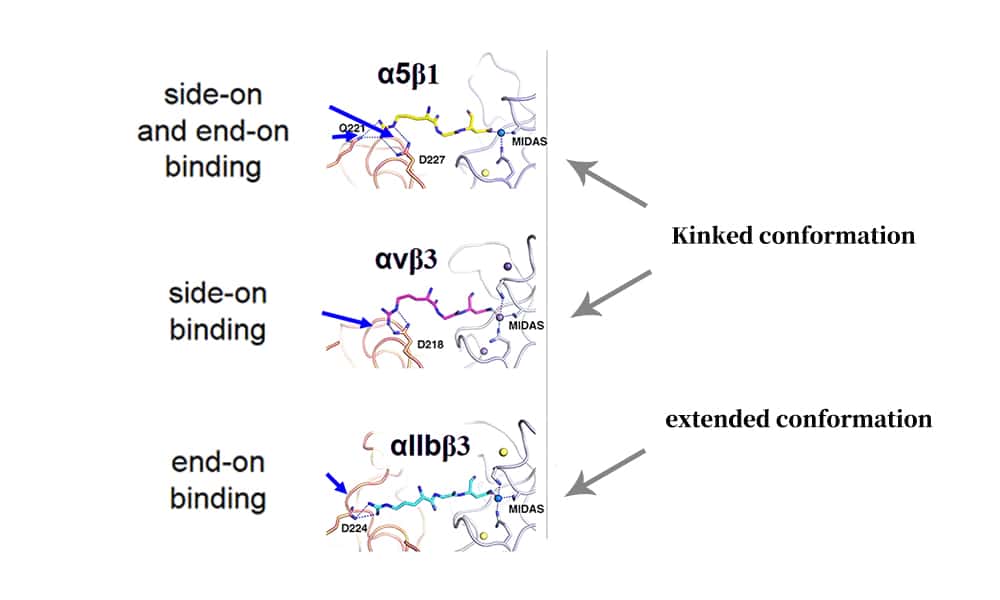
Cyclic RGD Peptides
Linear RGD peptides have problems such as low binding affinity, rapid degradation by proteases, and lack of integrin type specificity, which limits their applications. The interaction mechanism between RGD and integrin αvβ3 is affected by the steric conformation of the peptide and the structural features of RGD. Therefore, the biological potency of linear peptides can be improved by reducing conformational space via cyclization. Linear RGD peptides can form cyclic through disulfide bonds, thioethers or rigid aromatic rings linkers. A comparison of the interactions of cyclic and linear peptides with integrins is as follows:
- The flexibility of the linear RGD structure leads to instability and makes it more sensitive to chemical degradation. Cyclic peptides are more stable because of the rigidity of their ring structure. Therefore, cyclic RGD is commonly used to improve the binding properties of RGD peptides.
- The binding affinity between cyclic RGD peptide and integrin αvβ3 is much stronger and quicker than that of linear ligand. The flexibility of linear peptides makes it easier to form hydrogen bonds than cyclic RGD peptides that affects the binding ability.
- The interaction energy between ions and cyclic RGD is much stronger than that of the linear RGD system by the well shield to lessen attacks by free water molecules.
The model sequence of cyclic RGD peptide is c(RGDxX), and in-depth analyses of its structure-activity relationship show that there is a D-configuration (i.e., D-Phe, D-Tyr, D-Trp) aromatic amino acid at position 4 (residue x), which is critical for αvβ3 binding affinity. Residue X, the amino acid at position 5, has almost no effect on biological function. One of the first cyclic compounds that was developed and used in cellular studies was c(RGDfV). Subsequently, a series of functionalized cyclic penta-peptides were developed such as c(RGDfK), c(RGDfE), c(RGDyK) and c(RGDfC).
RGD Peptide Applications
Cancer
Integrins are considered promising targets for cancer therapy as well as the treatment of non-malignant angiogenic diseases since they are highly expressed on the endothelium during tumor angiogenesis. Integrin αvβ3 can specifically recognize RGD peptides that are designed to target integrins for cancer therapy.
Cilengitide is a cyclic RGD pentapeptide [c(RGDf(N Me)V)], which is yielded by N-Methylation of cyclic peptide c(RGDfV). The drug is the first anti-angiogenic small molecule targeting integrin αvβ3 that induces apoptosis in growing endothelial cells by preventing integrin from interacting with their ECM ligands. Cilengitide can be used to treat glioblastoma, however, neither by itself nor in conjunction with classic anticancer treatments has displayed to alter progression or improve survival.
CEND-1, also known as iRGD, is a bifunctional cyclic peptide that binds to the RGD motif and the integrin αV receptor to target tumors. Combinded with neuropilin-1, the delivery of anticancer drugs to tumors is improved by converting the solid tumor microenvironment into a temporary drug pipeline.
Diagnostics
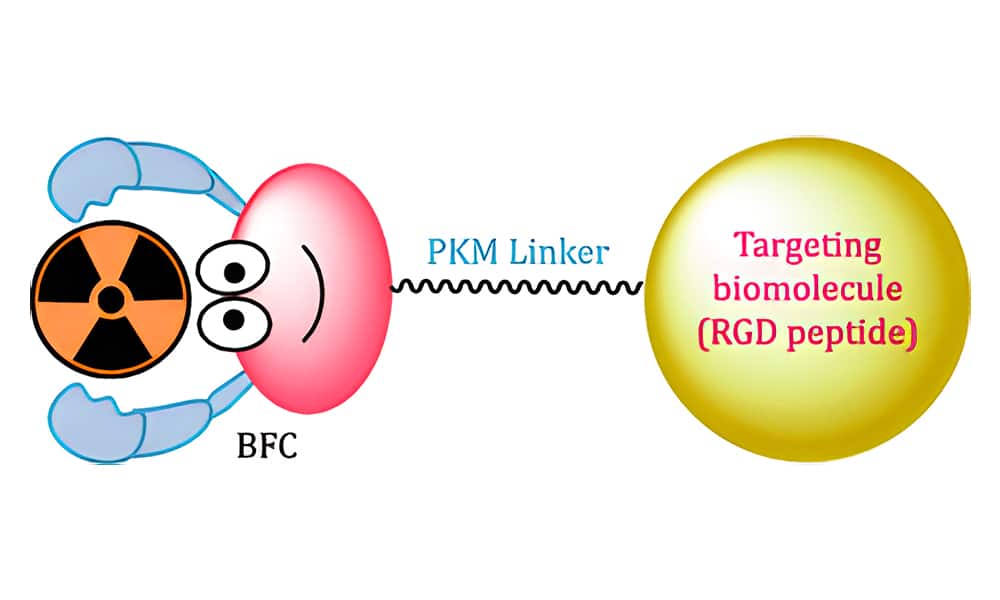
Integrin αvβ3 is not only an important biological target for the development of anti-angiogenic drugs, but also can be used as a molecular imaging probe for early tumor diagnosis. Because of RGD peptides have high affinity and specificity for integrin αvβ3, they are the basis for the majority of integrin-targeted imaging tracers. The structure of integrin-targeted radioactive tracers consists of the following three parts:
- RGD peptide: It acts as a “vehicle” to carry the isotope to integrins expressed on activated endothelial cells of tumor tissues.
- BFC: It is a bifunctional coupling agent that can connect appropriate radionuclides to RGD peptide.
- PKM: Pharmacokinetic Modifying Linker, which is frequently used to improve the excretion kinetics of radiotracers.
Scientists have studied several RGD peptide-based PET tracers to monitor tumor treatment response, including [18F]Galacto-RGD、[18F]Fluciclatide、[18F]RGD-K5、[18F]FPPRGD2、[18F]Alfatide、[68Ga]NOTA-RGD and [68Ga]NOTA-PRGD2. This could be useful for detecting malignancies and predicting short-term outcomes.
Drug Delivery
Numerous issues hinder conventional drug delivery techniques, including poor pharmacokinetics, off-target effects, and limited solubility. One of the methods used for improvement is nanoparticles, which can enhance permeability and retention to help selective accumulation of drugs into tumor sites, thereby increasing the drug’s efficacy and minimizing its negative effects.
Drug side effects from chemotherapy include nausea, vomiting, and hair loss. Chemotherapeutic drugs are wrapped in nanoparticles and modified with RGD ligands to target cancer cells expressing integrin αvβ3. Researchers have used RGD-conjugated nanomaterials to deliver the chemotherapeutics such as docetaxel, paclitaxel, and Gemcitabine to cancer cells.
Tissue Engineering
The goal of tissue engineering is to replace lost or damaged tissues in the body with biological materials that possess the ability to adhere to cells. Adhesion peptides are often utilized to engage and activate integrin receptors on the cell surface, thereby mediating cell attachment, proliferation, and differentiation. The most widely studied adhesion peptide is RGD that has been shown to be effective in guiding cells to attach to a variety of different materials, such as vascular tissue, bone tissue, and eye tissue.
- Vascular tissue: Inhibition of platelet adhesion, improvement of cell infiltration and enhancement of endothelialization are attributed to the use of RGD functionalized grafts in vascular tissue. Besides, RGD immobilized into cardiac tissue scaffolds can promote cell adhesion to the matrix, prevent cell apoptosis, and accelerate cardiac tissue regeneration.
- Bone tissue: RGD-coated titanium implants have positive effects in bone tissue. It can improve the attachment and differentiation of osteoblasts and enhance bone healing.
- Eye tissue: RGD-alginate hydrogels have raised increasing interest as effective strategies to promote the derivation and transplantation of stem cell retinal tissue as well as to enhance the formation of other pigmented, neural, or epithelial tissues.
Conclusion
RGD peptide is a potent integrin inhibitor and its interaction with integrin receptors is a promising tool for drug therapy and cancer research. Qyaobio provides a range of cyclic RGD peptides, which have rigid conformations and generally have higher metabolic stability than linear peptides. You can learn about our cyclic RGD peptide product information through the online store. If you are unable to find the derivative your desired, please contact our custom synthesis service with your request.