Stapled Peptide
Peptide stapling can enhance the pharmacologic performance of peptides.
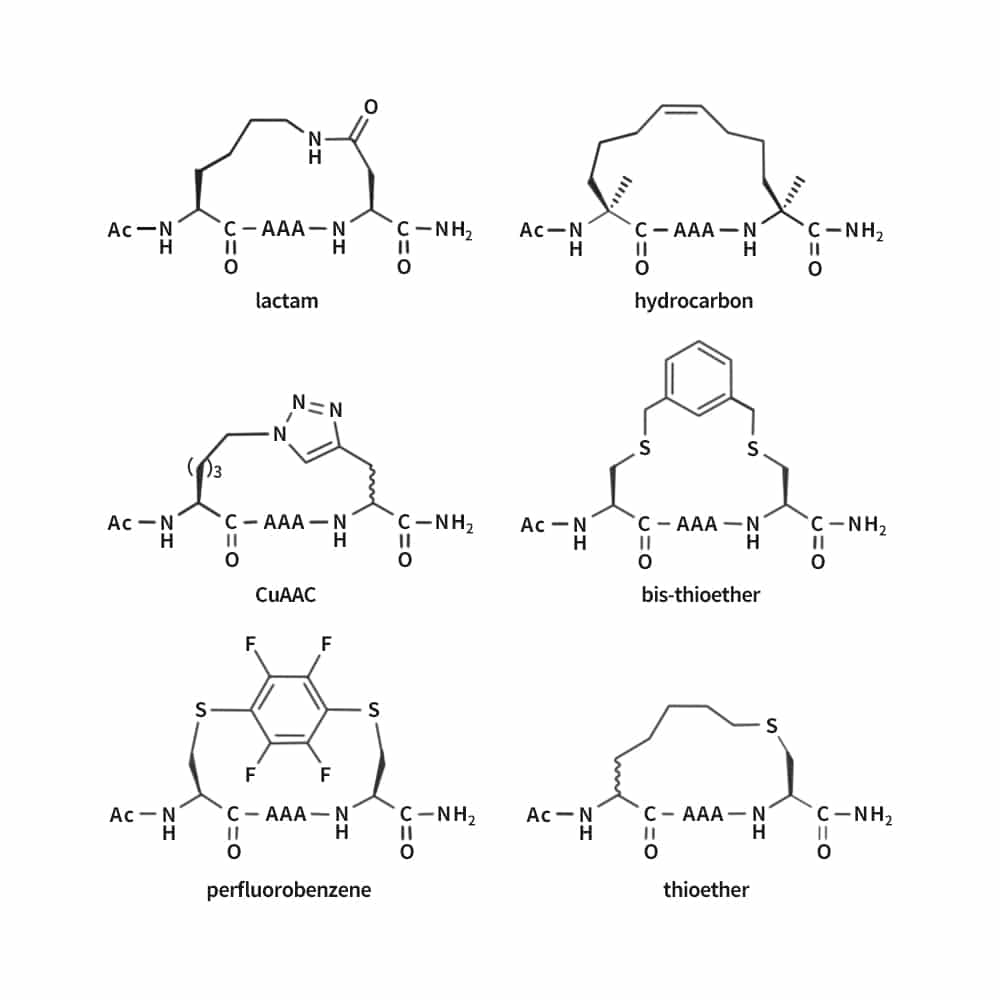
The stapled peptide is a short peptide with a typical alpha-helical conformation, it is constrained by the synthetic staple or brace. The staple is a covalent linkage between two amino acids side-chains, and forms as a peptide macrocycle. Staples refer to the covalent linkage of two independent entities, peptides with multiple and tandem staples are referred to as stitched peptides. Peptide stapling is applied notably to enhance the pharmacologic performance of peptides.
Introducing synthetic braces (staples) can lock the specific conformation of peptides, in order to reduce conformational entropy. This method can increase target affinity and cell penetration, and protect against proteolytic degradation. Although various strategies are applied to constrain α-helices, no mater non-covalent or covalent stabilization techniques. The all-hydrocarbon covalent link of peptide staple is proved to improve the stability and cell penetrability. Peptides staples are normally synthesized by ring-closing metathesis (RCM), peptide stapling technology are applied to numerous peptide templates, as well as other therapeutic targets from infectious diseases to metabolism.
Stapled Peptide Synthesis
Hydrocarbon stapled peptides are peptides locked into bioactive alpha-helical conformation by site-specific introduction of an all-hydrocarbon staple. The peptide stapling is ideal to overcome the limitations of two classes of therapeutic agents (small molecules and protein biologics) in targeting intra-cellular protein-protein interactions (PPI).
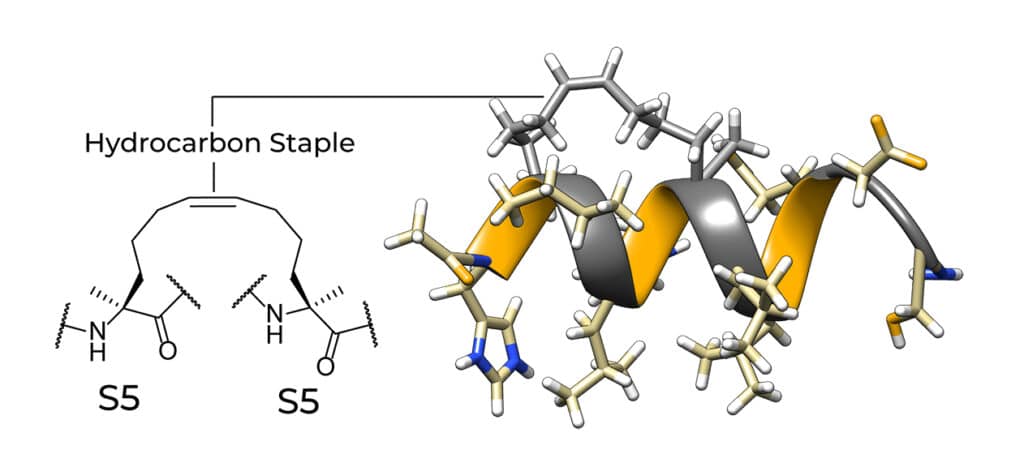
Normally, small molecules only work on proteins with specific features on the surface, and most protein biologics cannot penetrate into cells. Stapled peptides have locked α-helical structure (the most common protein secondary structures), and can penetrate cells easily. Stapled peptide is a rapidly emerging class of novel-generation drugs. Stapled peptides can combine the synthetic manipulability and cell-penetrating ability of small molecules, with three-dimensionality and versatile target recognition ability of biologics.
Qyaobio develops stapled peptides structures to satisfy professional requirements. Our technical team will discuss structure design with you at any time.
Stapled Peptide Chemistry
Different stapling chemistry can facilitate research and project development, we are able to provide a comprehensive list of stapled peptide synthesis: ring-closing metathesis, lactamization, click chemistry, thioether formation.
Grubbs catalyst of Stapled Peptides
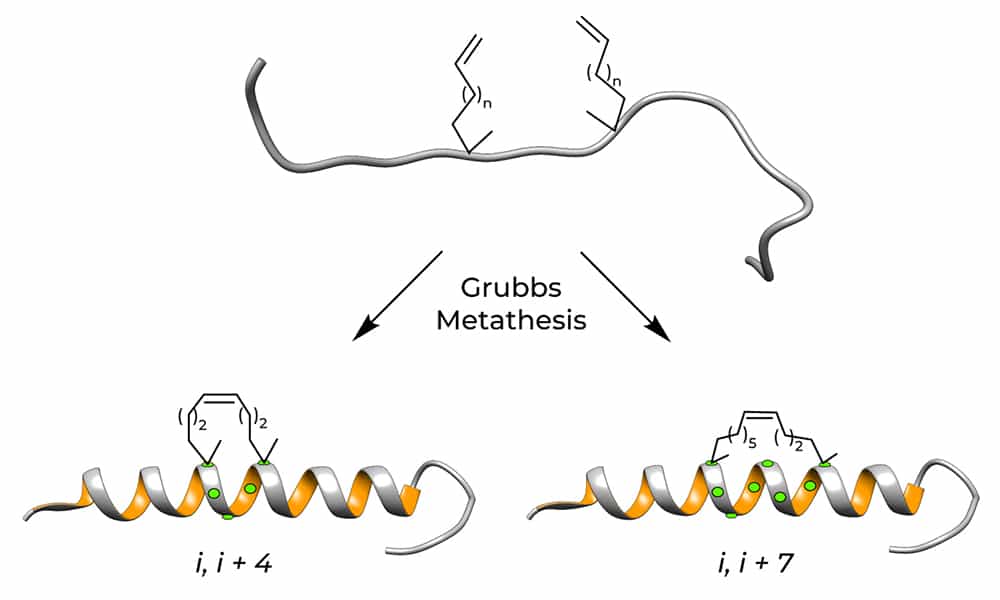
The first synthesis method of stapled peptide is Grubbs catalyst. It applies olefin metathesis to incorporate hydrocarbon staples into peptides. Two distinct conformational strategies are used to induce and stabilize the α-helical structure. Such as: α, α-di-substitution (helix nucleation by α-methylation), macro-cyclic bridge formation (conformational constraint). There are two different hydrocarbon staples in the fires, it demonstrates the stabilized α-helix structure in peptides.
Click Chemistry of Stapled Peptides
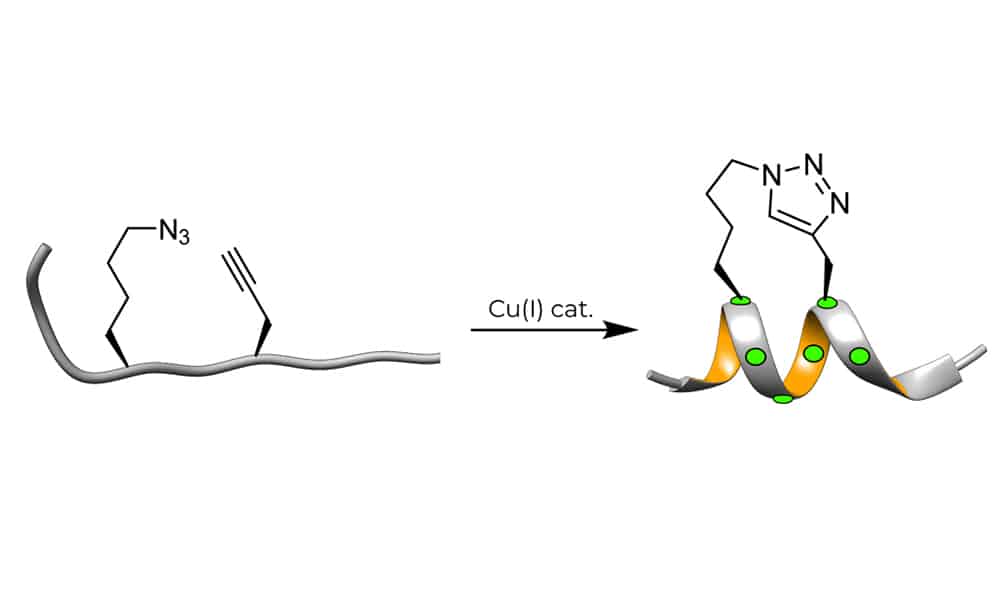
The high efficiency and mild conditions of click reaction result in facile synthesis of triazole-stapled peptides. This method combine the ease of synthesis with necessary unnatural amino acids. Such as the L-Nle(εN3) and D-Pra (D-propargylalanine) can be applied for the generation of single triazole-stapled peptides.
Stapling Configurations
The hydrocarbon stapled peptides are synthesized by solid-phase peptide synthesis (SPPS), where the incorporated crosslinks genetae with the α, α-disubstituted amino acids bearing olefinic chains of variable lengths at positions. Such as: I & I+3, I and I+4 or I and I+7 in the peptide sequence (I represent the first staple position).
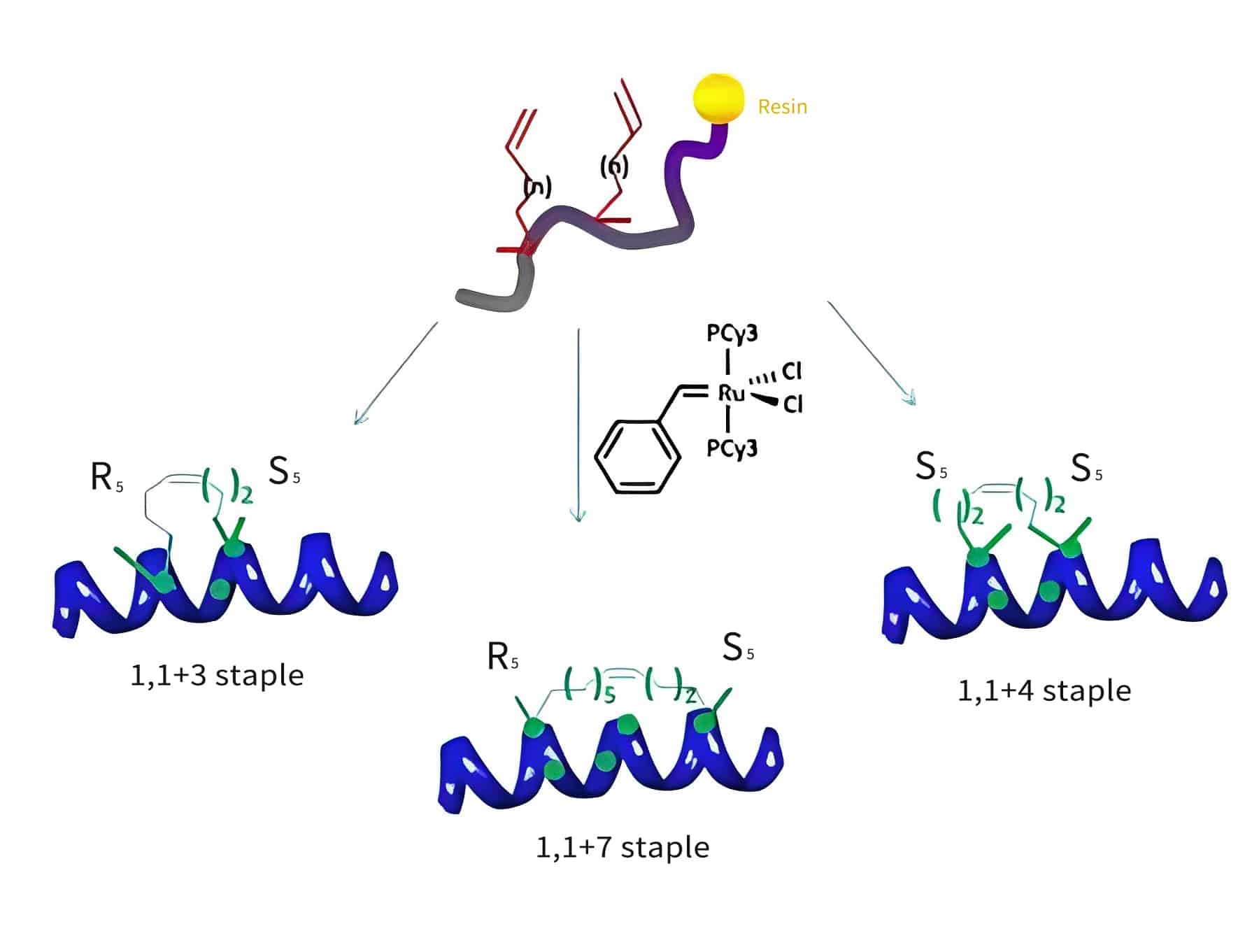
I & I+3
In I & I+3 stapled peptides, two amino acids are between the staple.
I & I+4
Three amino acids are between the I and I+4 staples. I & I+4 stapled peptides generate the most optimally stabilized pattern.
I & I+7
Six amino acids are between the I & I+7 staples.
The stapled peptides design allows incorporation o f non-natural amino acids at specific site positions, in order to form the staples (hydrocarbon cross-link) in the desired peptide. The modified hydrocarbon-stapled peptides are helical, relatively protease resistant, cell-permeable with increased bind affinity. In addition, hydrocarbon stapling provides a novel strategy in experimental and therapeutic modulation of protein-protein interactions (PPI) and vivo pharmacokinetics.
Stapled Peptides in Drug Design
The hydrocarbon staples confer high levels of α-helical content in peptides, this also result in bio-property alternation of stapled peptides.
- Higher target affinity of 5 to 5000 time increase
- High proteolytic resistance and long serum half-life
- Cell penetration by endocytic vesicle trafficking
- Proteins targeting of extracellular or intracellular
- Protein-protein interaction (PPI) disruption
- Non-immuneogenicity
- Viable pharmacokinetics and stability in vivo
Protein Targets of Stapled Peptides
As stapled peptides are studied in the proteins targeting of relevant diseases, such as cancer, diabetes, HIV, and atherosclerosis. The main proteins including:
- B-cell lymphoma (Bcl-2)
- B-cell lymphoma-extra large (Bcl-xL)
- Bcl-2-associated X protein
- Glucoskinase (GK)
- Induced myeloid leukemia cell differentiation (Mcl-1)
- Murine double minute 2 (Mdm2)
- ATP-binding cassette transporter (ABCA1)
- HIV-1 capsid and HIC-1 gp41
- Estrogen receptor
Modifications of Stapled Peptides
Stapled peptide modifications are in two typical categories: fluorescent labeling, affinity tagging. The most common moieties of fluorescent labeling on N-terminus are luciferin, which are applied for research of biophysical characterization and intracellular uptake. While affinity tagging are biotin, which for biophysical characterization and assessment in vitro target interaction. The flexible molecular spacer to isolate the core modification of stapled peptides, including:
- N-acetylation
- Linker attachment of β-alanine, mini-PEG, etc.
- Fluorescent labeling of FITC, 5-FAM, etc.
Call Us
+86(021)-50795728
+86(027)-60707970
